 Multiple Choice Questions
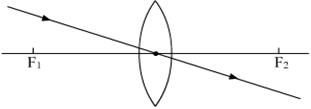
Multiple Choice QuestionsStudy the following ray diagrams:
i
. 
ii.
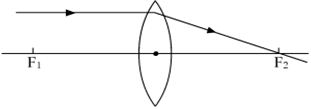
iii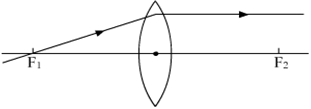
iv. 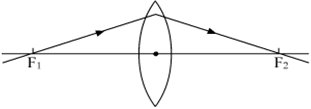
The diagrams showing the correct path of the ray after passing through the lens are:
II and III only
I and II only
I, II and III
I, II and III
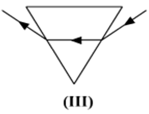
Out of the five incident rays shown in the figure find the three rays that are obeying the laws of refraction and may be used for locating the position of image formed by a convex lens:
1, 2 and 3
2, 3 and 4
3, 4 and 5
3, 4 and 5
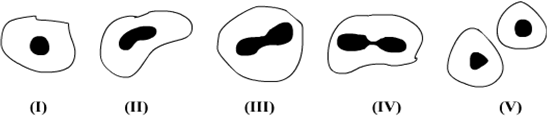
A student after observing a slide showing different stages of binary fission in Amoeba draws the following diagrams. However these diagrams are not in proper sequence:
The correct sequence is:
I, V, IV, III, II
I, III, IV, V, II
I, V, III, IV, II
I, V, III, IV, II
I, V, III, IV, II
Select the correct statements for the process of budding in yeast:
I. A bud arises from a particular region on a parent body.
II. A parent cell divides into two daughter cells, here the parental identity is lost.
III. Before detaching from the parent body a bud may form another bud.
IV. A bud when detaches from the parent body grows into a new individual.
I, II and III
II, III and IV
III, IV and I
III, IV and I
C.
III, IV and I
Budding is a type of asexual reproduction in which a new organism is formed from a bud of an existing organism. A small bud is formed at a specific position on the parent cell. The nucleus of parent cells splits and a part of it enters inside the newly formed bud. The bud develops into a new cell or daughter organism. The new organism remains attached to the parent organism till it gets matured. After attaining maturity it separates from the parent body.
Study the different conclusions drawn by students of a class on the basis of observations of preserved/available specimens of plants and animals.
I. Potato and sweet potato are analogous organs in plants.
II. Wings of insects and wings of birds are homologous organs in animals.
III. Wings of insects and wings of bats are analogous organs in animals.
IV. Thorns of citrus and tendrils of cucurbita are analogous organs in plants.
I, and II
II and IV
I and III
I and III
You have potato, carrot, radish, sweet potato, tomato and ginger bought from the market in your jute bag. Identify two vegetables to represent the correct homologous structures.
Potato and tomato
Carrot and tomato
Potato and sweet potato
Potato and sweet potato
In the figure, the parts marked A, B and C is sequentially: 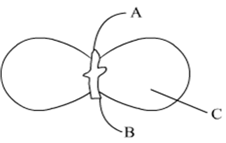
Plumule, Radicle and Cotyledon
Radicle, Plumule and Cotyledon
Plumule, Cotyledon and Radicle
Plumule, Cotyledon and Radicle
While performing the experiment to trace the path of a ray of light passing through a glass prism, four students marked the incident ray and the emergent ray in their diagrams in the manner shown below.
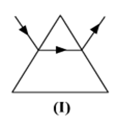
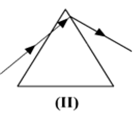

 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeHow many vertical columns are there in the modern periodic table and what are they called?
