 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeCopper crystallises with face centred cubic unit cell. If the radius of a copper atom is 127.8 pm, calculate the density of the copper metal.
(Atomic mass of Cu = 63.55 u and Avogadro’s number NA = 6.02 x 1023 mol-1)
Iron has a body centred cubic unit cell with the cell dimension of 286.65 pm. The density of iron is 7.87 g cm-3. Use this information to calculate Avogadro’s number. (Atomic mass of Fe = 56.0 u)
The reaction N2(g) + O2(g)Â Â Â 2NO(g), contributes to air pollution whenever a fuel is burnt in air at a high temperature. At 1500 K, equilibrium constant K for it is 1.0 x 10-5. Suppose in a case [N2] = 0.80 mol L-1and [O2] = 0.20 mol L-1Â before any reaction occurs. Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of the reactants and the product after the mixture has been heated to 1500 K.
The electrical resistance of a column of 0.05 M NaOH solution of diameter 1cm and length 50
cm is 5.55 x 103Â ohm. Calculate its resistivity, conductivity and molar conductivity.
Write three distinct features of chemisorptions which are not found in physisorptions.
Explain each of the following observations:
(i) With the same d-orbital configuration (d4), Cr2+Â is a reducing agent while Mn3+Â is an oxidising agent.
(ii) Actinoids exhibit a much larger number of oxidation states than the lanthanoids.
(iii) There is hardly any increase in atomic size with increasing atomic number in a series of transition metals.
Name of the following coordination entities and describe their structure:
(i) [Fe (CN)6]4-
(ii) [Cr (NH3)4Cl2]+
(iii) [Ni (CN) 4]2-
(Atomic numbers Fe = 26. Cr = 24, Ni = 28(i) [Fe (CN)6]4-
IUPAC name: Hexacyanoferrate (II)
Structure: Oxidation state of iron is + 2
Fe2+: Electronic configuration is 3d6 4s° 4p°
Orbitals of Fe2+Â ions:
 ![]()
As CN-Â is a strong field ligand, it causes the pairing of unpaired 3d electrons
 ![]()
Â
Since there are six ligands around the central metal ion, the most feasible hydrization is d2sp3.
d2sp2Â hybridized orbitals of Fe2+Â are:
 ![]()
Â
6 electron pairs from CN-1Â ions occupy the six hybrid d2sp3Â orbitals
Then,
 
Hence, the structure of [Fe (CN)6]4- is octahedral.
(ii) [Cr (NH3)4Cl2] +
Name: Tetraamminedichlorido chromium (III)
Electronic configuration of Cr: 3d4Â 4s2
Electronic configuration of Cr3+: 3d3
Â
 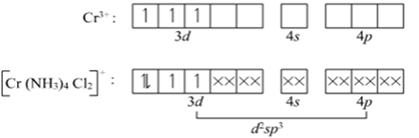
Structure is octahedral with d2sp3Â hybridization.
(iii) [Ni (CN) 4]2-
Name: Tetracyanonickelate (II)
Structure: Here oxidation state of Ni is + 2
Ni + 2: Electronic configuration is 3d8Â 4s0Â 4p0
Orbitals of Ni2+Â ion
Â
 ![]()
As CN-1is a strong field ligand, it causes the pairing of unpaired 3d electrons.
 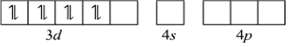
Â
Since, there are four ligands around the central metal ion, the most feasible hybridization is dsp2
Â
 ![]()
4 electron pairs from CN-1 ions occupy the four hybrid dsp2 orbitals
Then,
 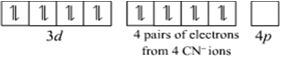
Â
Hence, the structure of [Ni(CN)4]2- is square planar.
Write a reaction which shows that all the carbon atoms in glucose are linked in a straight chain.
