 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWrite the equations involved in the following reactions:
(i) Reimer − Tiemann reaction
(ii) Williamson synthesis
Write the names of monomers used for getting the following polymers:
(i) Bakelite
(ii) Neoprene
(a) Draw the structures of major monohalo products in each of the following reactions :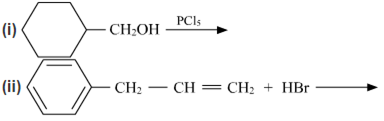
(b) Which halogen compound in each of the following pairs will react faster in SN2 reaction:
(i) CH3Br or CH3I
(ii) (CH3)3C−Cl or CH3−Cl
Account for the following:
(i) Primary amines (R-NH2) have higher boiling point than tertiary amines (R3N).
(ii) Aniline does not undergo Friedel - Crafts reactions:
(iii) (CH3)2NH is more basic than (CH3)3N in an aqueous solution.
OR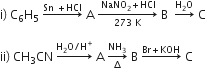
(i) The greater the extent of intermolecular hydrogen bonding, greater is the boiling point of the compound. Primary amines are involved in intermolecular hydrogen bonding, whereas tertiary amines do not have any available hydrogen atoms, and hence they are not involved in any intermolecular hydrogen bonding. Thus, primary amines (R-NH2) have higher boiling point than tertiary amines (R3N).
(ii) A Friedel-Crafts reaction is carried out in the presence of a lewis acid such as AlCl3. Aniline being basic in nature reacts with AlCl3 to form a salt (as shown in the following equation).

Due to the positive charge on the N-atom, electrophilic substitution in the benzene ring is deactivated. Hence, aniline does not undergo the Friedel-Crafts reaction.
(iii) The order of basic strength of aliphatic amines in the aqueous phase, is based on following factors:
Steric factor: Alkyl group is larger than hydrogen atom that causes steric hindrance to attack of acid. As the number of alkyl group increases from primary to tertiary. The steric hindrance also increases in the same direction.
Solvation of ions: when amines are dissolved in water, they form hydrogen bonds with a water molecule and release hydration energy; in the process converting themselves to the protonated amines to get stabilized. Greater the extent of hydrogen bonding, greater is the hydration energy released and more is the stability of the protonated amine; thus greater is the tendency of the amine to form cation leading to the greater basic strength of the amine. So, the actual order of basic strength in aqueous phase is found to be:
Secondary > Tertiary > Primary
Therefore, secondary amines are the strongest base in aqueous solution.

Define the following terms as related to proteins:
(i) Peptide linkage
(ii) Primary structure
(iii) Denaturation
On the occasion of World Health Day, Dr Satpal organised a 'health camp' for the poor farmers living in a nearby village. After the check-up, he was shocked to see that most of the farmers suffered from cancer due to regular exposure to pesticides and many were diabetic. They distributed free medicines to them. Dr. Satpal immediately reported the matter to the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC). On the suggestions of NHRC, the government decided to provide medical care, financial assistance, setting up of super-speciality hospitals for treatment and prevention of the deadly disease in the affected villages all over India.
(i) Write the values shown by
(a) Dr. Satpal
(b) NHRC
(ii) What type of analgesics are chiefly used for the relief of pains of terminal cancer?
(iii) Give an example of artificial sweetener that could have been recommended to diabetic patients.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) Define the following terms :
(i) Molarity
(ii) Molal elevation constant (Kb)
(b) A solution containing 15 g urea (molar mass = 60 g mol–1) per litre of the solution in water has the same osmotic pressure (isotonic) as a solution of glucose (molar mass = 180 g mol–1) in water. Calculate the mass of glucose present in one litre of its solution.
OR
(a) What type of deviation is shown by a mixture of ethanol and acetone? Give reason.
(b) A solution of glucose (molar mass = 180 g mol–1) in water is labelled as 10% (by mass). What would be the molality and molarity of the solution?
(Density of solution = 1.2 g mL–1)
(a) Complete the following equations :
(i) Cr2O72- + 2OH- --->
(ii) MnO4- + 4H+ + 3e- --->
(b) Account for the following :
(i) Zn is not considered as a transition element.
(ii) Transition metals form a large number of complexes.
(iii) The E° value for the Mn3+/Mn2+ couple is much more positive than that for Cr3+/Cr2+ couple.
OR
(i) With reference to structural variability and chemical reactivity, write the differences between lanthanoids and actinoids.
(ii) Name a member of the lanthanoid series which is well known to exhibit +4 oxidation state.
(iii) Complete the following equation :
MnO4- + 8H+ + 5e---->
iv) Mn3+ is more paramagnetic than Cr3+.
(a) Write the products formed when CH3CHO reacts with the following reagents:
(i) HCN
(ii) H2N−OH
(iii) CH3CHO in the presence of dilute NaOH
(b) Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(i) Benzoic acid and Phenol
(ii) Propanal and Propanone
OR
(a) Account for the following:
(i) Cl−CH2COOH is a stronger acid than CH3COOH.
(ii) Carboxylic acids do not give reactions of the carbonyl group.
(b) Write the chemical equations to illustrate the following name reactions:
(i) Rosenmund reduction
(ii) Cannizzaro's reaction
(c) Out of CH3CH2−CO−CH2−CH3 and CH3CH2−CH2−CO−CH3, which gives iodoform test?
