Short Answer Type
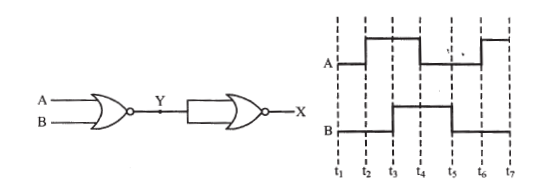
Short Answer TypeDraw the output waveform at X, using the given inputs A and B for the logic circuit shown below. Also, identify the logic operation performed by this circuit.
Name the semiconductor device that can be used to regulate an unregulated dc power supply. With the help of I-V characteristics of this device, explain its working principle.
Draw the transfer characteristic curve of a base biased transistor in CE configuration. Explain clearly how the active region of the V0 versus Vi curve in a transistor is used as an amplifier.
(i) Define modulation index.
(ii) Why is the amplitude of modulating signal kept less than the amplitude of carrier wave?An electron and a photon each have a wavelength 1.00 nm. Find
(i) their momenta,
(ii) the energy of the photon and
(iii) the kinetic energy of electron.Draw a schematic diagram showing the (i) ground wave (ii) sky wave and (iii) space wave propagation modes for EM waves.
Write the frequency range for each of the following:
(i) Standard AM broadcast
(ii) Television
(iii) Satellite communicationDescribe Young's double slit experiment to produce interference pattern due to a monochromatic source of light. Deduce the expression for the fringe width.
Use Huygens principle to verify the laws of refraction.
Proof of Snell’s law of Refraction using Huygens wave theory is:
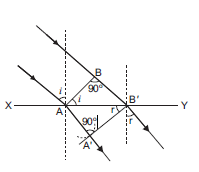
As seen in the fig. above let XY be a surface separating the two media ‘1’ and ‘2’. Let v1 and v2 be the speeds of waves in these media.
A plane wavefront AB in the first medium is incident obliquely on the boundary surface XY and its end A touches the surface at A at time t = 0 while the other end B reaches the surface at point B after time-interval t.
Here, ![]()
As the wavefront AB advances, it strikes the points between A and B¢ of boundary surface.
According to Huygens principle, secondary spherical wavelets emanate from these points, which travel with speed v1 in the first medium and speed v2 in the second medium.
Secondary wavelet starting from A, traverses a distance AA’ = v2t in second medium in time t. In the same time, point of wavefront traverses a distance in first medium and reaches B’, from where the secondary wavelet starts.
So, ![]() and AA’ = v2t.
and AA’ = v2t.
Assuming A as centre, we draw a spherical arc of radius AA’ (= v2t) and draw tangent B’A’ on this arc from B’. As the incident wavefront AB advances, the secondary wavelets start from points between A and B’, one after the other and will touch A’B’ simultaneously.
According to Huygens principle A’B’ is the new position of wavefront AB in the second medium. Hence A’B’ will be the refracted wavefront.
First law: As AB, A’B’ and surface XY are in the plane of paper, therefore the perpendicular drawn on them will be in the same plane. As the lines drawn normal to wavefront denote the rays, therefore we may say that the incident ray, refracted ray and the normal at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
This is the first law of refraction.
Second law: Let the angle made by incident wavefront be i and angle made by the refracted wavefront A’B’ be r.
In ![]()
![]()
![]() ... (1)
... (1)
Similarly, in right-angled triangle, <AA'B,
![]()
Therefore,
![]()
![]()
Now, dividing equation (1) by (2), we have ![]()
The ratio of sine of angle of incidence and the sine of angle of refraction is a constant and is equal to the ratio of velocities of waves in the two media. This is the second law of refraction, and is called the Snell’s law.
(a) Describe briefly, with the help of suitable diagram, how the transverse nature of light can be demonstrated by the phenomenon of polarization.
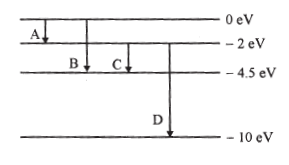
(b) When unpolarized light passes from air to a transparent medium, under what condition does the reflected light get polarized?The energy levels of a hypothetical atom are shown below. Which of the shown transitions will result in the emission of a photon of wavelength 275 nm?
Which of these transitions correspond to emission of radiation of (i) maximum and (ii) minimum wavelength?