 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeA convex lens made up of glass of refractive index 1.5 is dipped, in turn, in (i) a medium of refractive index 1.65, (ii) a medium of refractive index 1.33.
(a) Will it behave as a converging or a diverging lens in the two cases?
(b) How will its focal length change in the two media?Draw a plot showing the variation of photoelectric current with collector plate potential for two different frequencies, v1 >v2 , of incident radiation having the same intensity. In which case will the stopping potential be higher? Justify your answer.
Write briefly any two factors which demonstrate the need for modulating a signal.
Draw a suitable diagram to show amplitude modulation using a sinusoidal signal as the modulating signal.
Use the mirror equation to show that:
(a) an object placed between f and 2f of a concave mirror produces a real image beyond 2f.
(b) a convex mirror always produces a virtual image independent of the location of the object.
(c) an object placed between the pole and focus of a concave mirror produces a virtual and enlarged image.
(a) Using de Broglie’s hypothesis, explain with the help of a suitable diagram, Bohr’s second postulate of quantization of energy levels in a hydrogen atom.
(b) The ground state energy of hydrogen atom is –13.6 eV. What are the kinetic and potential energies of the electron in this state?You are given a circuit below. Write its truth table. Hence, identify the logic operation carried out by this circuit. Draw the logic symbol of the gate it corresponds to. 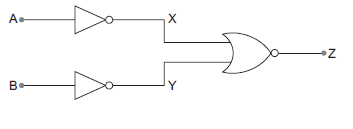
A compound microscope uses an objective lens of focal length 4 cm and eyepiece lens of focal length 10 cm. An object is placed at 6 cm from the objective lens. Calculate the magnifying power of the compound microscope. Also calculate the length of the microscope.
OR
A giant refracting telescope at an observatory has an objective lens of focal length 15 m. If an eyepiece lens of focal length 1.0 cm is used, find the angular magnification of the telescope.
If this telescope is used to view the moon, what is the diameter of the image of the moon formed by the objective lens? The diameter of the moon is 3.42 × 106 m and the radius of the lunar orbit is 3.8 × 108 m.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) Using Ampere’s circuital law, obtain the expression for the magnetic field due to a long solenoid at a point inside the solenoid on its axis.
(b) In what respect is a toroid different from a solenoid? Draw and compare the pattern of the magnetic field lines in the two cases.
(c) How is the magnetic field inside a given solenoid made strong?
State the working of a.c. generator with the help of a labelled diagram.
The coil of an a.c. generator having N turns, each of area A, is rotated with a constant angular velocity. Deduce the expression for the alternating e.m.f. generated in the coil.
What is the source of energy generation in this device?
OR
(a) Show that in an a.c. circuit containing a pure inductor, the voltage is ahead of current by 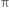 /2 in phase.
/2 in phase.
(b) A horizontal straight wire of length L extending from east to west is falling with speed v at right angles to the horizontal component of Earth’s magnetic field B.
(i) Write the expression for the instantaneous value of the e.m.f. induced in the wire.
(ii) What is the direction of the e.m.f.?
(iii) Which end of the wire is at the higher potential?
Working of ac generator:
When the armature coil is rotated in the strong magnetic field, the magnetic flux linked with the coil changes and the current is induced in the coil, its direction being given by Fleming’s right hand rule. Considering the armature to be in vertical position and as it rotates in anticlockwise direction, the wire ab moves upward and cd downward, so that the direction of induced current is shown in fig. In the external circuit, the current flows along B1RL B2.
The direction of current remains unchanged during the first half turn of armature. During the second half revolution, the wire ab moves downward and cd upward, so the direction of current is reversed and in external circuit it flows along B2RL B1. Thus the direction of induced emf and current changes in the external circuit after each half revolution.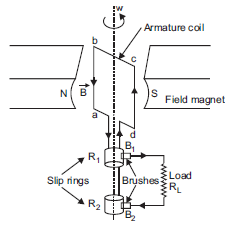
Let, N be the number of turns in the coil,
f is the frequency of rotation,
A is the area of coil,
B is the magnetic induction.
Then, the induced emf is given by, 
We can see that the emf and current produced is alternating.
Current produced by an ac generator cannot be measured by moving coil ammeter; because the average value of ac over full cycle is zero.
The source of energy generation is the mechanical energy of rotation of armature coil.
OR
Consider a coil of self-inductance L and negligible ohmic resistance. An alternating potential difference is applied across the ends. The magnitude and direction of AC is changing periodically, changing the magnetic flux. So, an emf is induced and produced in the coil. The instantaneous value of alternating voltage applied is given by,
V = Vo sin w t
Instantaneous induced emf is, 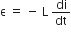
According to Kirchhoff’s second law in closed circuit, we get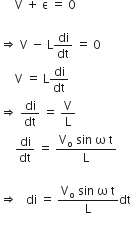
Integrating with respect to time ‘t’,
which is the required expression for current. ;
;
where, 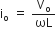 is the peak value of alternating current.
is the peak value of alternating current.
From the above equations we can say that the current lags behind the applied voltage by an angle .
b)
i) Induced emf, = BHvL ; where BH is horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field directed from South to North.
ii) West to East
iii) East end of the wire is at higher potential
(a) State the principle of the working of a moving coil galvanometer, giving its labelled diagram.
(b) “Increasing the current sensitivity of a galvanometer may not necessarily increase its voltage sensitivity.” Justify this statement.
(c) Outline the necessary steps to convert a galvanometer of resistance RG into an ammeter of a given range.
