 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeState the importance of coherent sources in the phenomenon of interference.
In Young’s double slit experiment to produce interference pattern, obtain the conditions for constructive and destructive interference. Hence, deduce the expression for the fringe width.
How does the fringe width get affected, if the entire experimental apparatus of Young is immersed in water?
(a) State Huygens principle. Using this principle explain how a diffraction pattern is obtained on a screen due to a narrow slit on which a narrow beam coming from a monochromatic source of light is incident normally.
(b) Show that the angular width of the first diffraction fringe is half of that of the central fringe.
(c) If a monochromatic source of light is replaced by white light, what change would you observe in the diffraction pattern?
Huygen’s principle:
(i) Every point on a given wavefront may be regarded as a source of new disturbance.
(ii) The new disturbances from each point spread out in all directions with the velocity of light and are called the secondary wavelets.
(iii) The surface of tangency to the secondary wavelets in forward direction at any instant gives the new position of the wavefront at that time.
a) Diffraction of light at a Single slit
A single narrow slit is illuminated by a monochromatic source of light. The diffraction pattern is obtained on the screen placed in front of the slits. There is a central bright region called as central maximum. All the waves reaching this region are in phase hence the intensity is maximum. On both side of central maximum, there are alternate dark and bright regions, the intensity becoming weaker away from the center. The intensity at any point P on the screen depends on the path difference between the waves arising from different parts of the wave-front at the slit.
According to the figure, the path difference (BP – AP) between the two edges of the slit can be calculated.
Path difference, BP – AP = NQ = a sin 
Angle is zero at the central point C on the screen, therefore all path difference are zero and hence all the parts of slit are in phase. Due to this, the intensity at C is maximum. If this path difference is  , (the wavelength of light used), then P will be point of minimum intensity. This is because the whole wave-front can be considered to be divided into two equal halves CA and CB and if the path difference between the secondary waves from A and B is
, (the wavelength of light used), then P will be point of minimum intensity. This is because the whole wave-front can be considered to be divided into two equal halves CA and CB and if the path difference between the secondary waves from A and B is  , then the path difference between the secondary waves from A and C reaching P will be
, then the path difference between the secondary waves from A and C reaching P will be  /2, and path difference between the secondary waves from B and C reaching P will again be
/2, and path difference between the secondary waves from B and C reaching P will again be  /2. Also, for every point in the upper half AC, there is a corresponding point in the lower half CB for which the path difference between the secondary waves, reaching P is
/2. Also, for every point in the upper half AC, there is a corresponding point in the lower half CB for which the path difference between the secondary waves, reaching P is  /2. Thus, destructive interference takes place at P and therefore, P is a point of first secondary minimum.
/2. Thus, destructive interference takes place at P and therefore, P is a point of first secondary minimum.
b)
Central bright lies between 
Therefore, Angular width of central bright fringe = 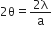
So, 1st diffraction fringe lies between 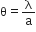 and
and 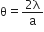
Therefore,
Angular width of first diffraction fringe is, 
So, 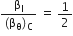
c) When monochromatic light is replaced by white light, each diffraction band splits into a number of colored bands. Angular width of violet being the least and that of red light is maximum.
