 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) Draw a labelled diagram of a moving coil galvanometer. Describe briefly its principle and working.
(b) Answer the following:
(i) Why is it necessary to introduce a cylindrical soft iron core inside the coil of a galvanometer?
(ii) Increasing the current sensitivity of a galvanometer may not necessarily increase its voltage sensitivity. Explain, giving reason.
b) Moving coil galvanometer: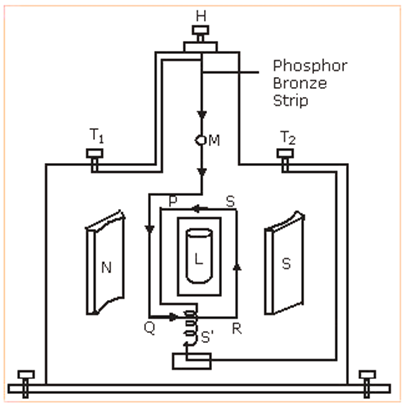
Principle: The underlying principle of moving coil galvanometer is that a current carrying coil, placed in a uniform magnetic field, experiences torque.
Consider a rectangular coil for which no. of turns = N
Are of cross-section is A = lb
Intensity of the uniform magnetic field = B
Current through the coil = I
Therefore,
Deflecting torque is given by,
BIL x b = BIA
For N number of turns,
 = NBIA
= NBIA
Restoring torque in the spring = k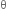
Therefore,
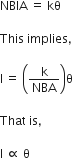
b) i) The soft iron coil in a galvanometer will make the field radial. Also, it increases the strength of the magnetic field.
ii) Current sensitivity in the galvanometer is given by, 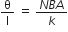
Voltage sensitivity in the galvanometer is given by, 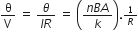
The above two equations imply that increasing the current sensitivity may not necessarily increase the voltage sensitivity.
(a) In Young's double slit experiment, describe briefly how bright and dark fringes are obtained on the screen kept in front of a double slit. Hence obtain the expression for the fringe width.
(b) The ratio of the intensities at minima to the maxima in the Young's double slit experiment is 9: 25. Find the ratio of the widths of the two slits.
(a) Describe briefly how a diffraction pattern is obtained on a screen due to a single narrow slit illuminated by a monochromatic source of light. Hence obtain the conditions for the angular width of secondary maxima and secondary minima.
(b) Two wavelengths of sodium light of 590 nm and 596 nm are used in turn to study the diffraction taking place at a single slit of aperture 2 × 10−6 m. The distance between the slit and the screen is 1·5 m. Calculate the separation between the positions of first maxima of the diffraction pattern obtained in the two cases.
