 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeDraw a block diagram of a detector for AM signal and show, using necessary processes and the waveforms, how the original message signal is detected from the input AM waves.
With what considerations in view, a photodiode is fabricated? State it’s working with the help of a suitable diagram.
Even though the current in the forward bias is known to be more than in the reverse bias, yet the photodiode works in reverse bias. What is the reason?Draw a circuit diagram of a transistor amplifier in CE configuration.
Define the terms:Answer the following questions:
(a) In a double slit experiment using light of wavelength 600 nm, the angular width of the fringe formed on a distant screen is 0.1°. Find the spacing between the two slits.
(b) Light of wavelength 5000 Å propagating in air gets partly reflected from the surface of water. How will the wavelengths and frequencies of the reflected and refracted light be affected? Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeA group of students while coming from the school noticed a box marked “Danger H.T. 2200 V” at a substation in the main street. They did not understand the utility of such a high voltage, while they argued; the supply was only 220 V. They asked their teacher this question the next day. The teacher thought it to be an important question and therefore explained to the whole class.
Answer the following questions:
(i) What device is used to bring the high voltage down to low voltage of a.c. current and what is the principle of its working?
(ii) Is it possible to use this device for bringing down the high dc voltage to the low voltage? Explain.
iii) Write the values displayed by the students and the teacher.
(a) State Ampere’s circuital law. Use this law to obtain the expression for the magnetic field inside an air cored toroid of average radius ‘r’, having ‘n’ turns per unit length and carrying a steady current I.
(b) An observer to the left of a solenoid of N turns each of cross section area ‘A’ observes that a steady current I in it flows in the clockwise direction. Depict the magnetic field lines due to the solenoid specifying its polarity and show that it acts as a bar magnet of magnetic moment m = NIA. 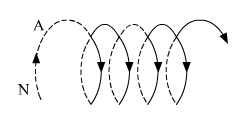
(a) Define mutual inductance and write its S.I. units.
(b) Derive an expression for the mutual inductance of two long co-axial solenoids of same length wound one over the other.
(c) In an experiment, two coils C1 and C2 are placed close to each other. Find out the expression for the emf induced in the coil C1 due to a change in the current through the coil C2.
(a) An electric dipole of dipole moment p⃗ consists of point charges +q and –q separated by a distance 2a apart. Deduce the expression for the electric field E⃗ due to the dipole at a distance x from the center of the dipole on its axial line in terms of the dipole moment p⃗. Hence show that in the limit x >> a, E⃗ → 2 p⃗/ (4p ε0 x3).
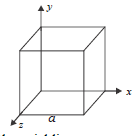
(b) Given the electric field in the region E⃗ = 2x i, find the net electric flux through the cube and the charge enclosed by it.
(a) Explain, using suitable diagrams, the difference in the behaviour of a
(i) conductor and
(ii) dielectric in the presence of external electric field. Define the terms polarization of a dielectric and write its relation with susceptibility.
(b) A thin metallic spherical shell of radius R carries a charge Q on its surface. A point charge Q/2 is placed at its centre C and another charge +2Q is placed outside the shell at a distance x from the centre as shown in the figure. Find
(i) the force on the charge at the centre of shell and at the point A,
(ii) the electric flux through the shell.
(a) Using Huygens’s construction of secondary wavelets explain how a diffraction pattern is obtained on a screen due to a narrow slit on which a monochromatic beam of light is incident normally.
(b) Show that the angular width of the first diffraction fringe is half that of the central fringe.
(c) Explain why the maxima at 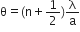 become weaker and weaker with increasing n.
become weaker and weaker with increasing n.
a) Diffraction of light at a Single slit
A single narrow slit is illuminated by a monochromatic source of light. The diffraction pattern is obtained on the screen placed in front of the slits. There is a central bright region called as central maximum. All the waves reaching this region are in phase hence the intensity is maximum. On both sides of the central maximum, there are alternate dark and bright regions, the intensity becoming weaker away from the center. The intensity at any point P on the screen depends on the path difference between the waves arising from different parts of the wave front at the slit.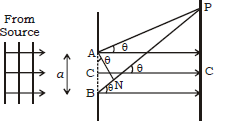
According to the figure, the path difference (BP – AP) between the two edges of the slit can be calculated.
Path difference, BP – AP = NQ = 
Angle 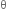 is zero at the central point C on the screen, therefore all path difference is zero and hence all the parts of the slit are in phase.
is zero at the central point C on the screen, therefore all path difference is zero and hence all the parts of the slit are in phase.
Due to this, the intensity at C is maximum. If this path difference is, (the wavelength of light used), then P will be the point of minimum intensity.
This is because the whole wave-front can be considered to be divided into two equal halves CA and CB and if the path difference between the secondary waves from A and B is  , then the path difference between the secondary waves from A and C reaching P will be
, then the path difference between the secondary waves from A and C reaching P will be  /2, and path difference between the secondary waves from B and C reaching P will again be
/2, and path difference between the secondary waves from B and C reaching P will again be  /2. Also, for every point in the upper half AC, there is a corresponding point in the lower half CB for which the path difference between the secondary waves, reaching P is
/2. Also, for every point in the upper half AC, there is a corresponding point in the lower half CB for which the path difference between the secondary waves, reaching P is  /2. Thus, destructive interference takes place at P, and therefore, P is a point of first secondary minimum.
/2. Thus, destructive interference takes place at P, and therefore, P is a point of first secondary minimum.
b)
Central bright lies between, 
Therefore, Angular width of central bright fringe = 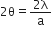
So, 1st diffraction fringe lies between 
Therefore,
Angular width of first diffraction fringe is, 
Hence proved.
c) As n increases, part of the slit contributing towards maximum decreases. Therefore, maxima gets weaker with increasing n.
