 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsABC is a triangle. Forces 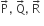 acting along IA, IB and IC respectively are in equilibrium, where I is incentre of ∆ABC. Then P : Q : R is
acting along IA, IB and IC respectively are in equilibrium, where I is incentre of ∆ABC. Then P : Q : R is
sin A : sin B : sin C

The normal to the curve x = a(cosθ + θ sinθ), y = a( sinθ - θ cosθ) at any point ‘θ’ is such that
it passes through the origin
it makes angle π/2 + θ with the x-axis
it passes through (aπ/2 ,-a)
it passes through (aπ/2 ,-a)
The area enclosed between the curve y = loge (x + e) and the coordinate axes is
1
2
3
3
A.
1
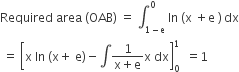
The parabolas y2 = 4x and x2 = 4y divide the square region bounded by the lines x = 4, y = 4 and the coordinate axes. If S1, S2, S3 are respectively the areas of these parts numbered from top to bottom; then S1 : S2: S3 is
1 : 2 : 1
1 : 2 : 3
2 : 1 : 2
2 : 1 : 2
The line parallel to the x−axis and passing through the intersection of the lines ax + 2by + 3b = 0 and bx − 2ay − 3a = 0, where (a, b) ≠ (0, 0) is
below the x−axis at a distance of 3/2 from it
below the x−axis at a distance of 2 /3 from it
above the x−axis at a distance of 3/ 2 from it
above the x−axis at a distance of 3/ 2 from it
Let f : R → R be a differentiable function having f (2) = 6, f′ (2) =(1/48) . Then 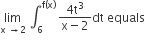
24
36
12
12
Let f (x) be a non−negative continuous function such that the area bounded by the curve y = f (x), x−axis and the ordinates x = π/4 and x = β > π/4 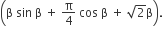 Then f (π/2) is
Then f (π/2) is
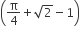
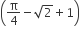
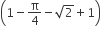
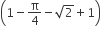
If the angle θ between the line 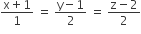 and the plane
and the plane  is such of sin θ = 1/3 the value of λ is
is such of sin θ = 1/3 the value of λ is
5/3
-3/5
3/4
3/4
