 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsAB is a vertical pole with B at the ground level and A at the top. A man finds that the angle of elevation of the point A from a certain point C on the ground is 60°. He moves away from the pole along the line BC to a point D such that CD = 7 m. From D the angle of elevation of the point A is 45°.
Then the height of the pole is
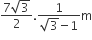
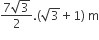
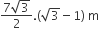
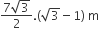
A die is thrown. Let A be the event that the number obtained is greater than 3. Let B be the event that the number obtained is less than 5. Then P (A ∪ B) is
3/5
0
1
1
A focus of an ellipse is at the origin. The directrix is the line x = 4 and the eccentricity is 1/2. Then the length of the semi−major axis is
8/3
2/3
5/3
5/3
A parabola has the origin as its focus and the line x = 2 as the directrix. Then the vertex of the parabola is at
(0, 2)
(1, 0)
(0,1)
(0,1)
The point diametrically opposite to the point P (1, 0) on the circle x2+ y2 + 2x + 4y − 3 = 0 is
(-3,4)
(-4,3)
(-3,-4)
(-3,-4)
The perpendicular bisector of the line segment joining P (1, 4) and Q (k, 3) has y−intercept − 4. Then a possible value of k is
1
2
-2
-2
The solution of the differential equation 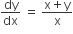 satisfying the condition y (1) = 1 is
satisfying the condition y (1) = 1 is
y = ln x + x
y = x ln x + x2
y = xe(x−1)
y = xe(x−1)
The mean of the numbers a, b, 8, 5, 10 is 6 and the variance is 6.80. Then which one of the following gives possible values of a and b?
a = 0, b = 7
a = 5, b = 2
a = 1, b = 6
a = 1, b = 6
D.
a = 1, b = 6
Mean of a, b, 8, 5, 10 is 6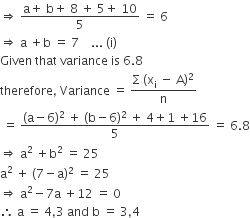
Statement − 1: For every natural number n ≥ 2 
Statement −2: For every natural number n ≥ 2,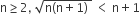
Statement −1 is false, Statement −2 is true
Statement −1 is true, Statement −2 is true, Statement −2 is a correct explanation for Statement −1
Statement −1 is true, Statement −2 is true; Statement −2 is not a correct explanation for Statement −1.
Statement −1 is true, Statement −2 is true; Statement −2 is not a correct explanation for Statement −1.
