 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsSuppose the cube x3– px + q has three distinct real roots where p > 0 and q > 0. Then which one of the following holds?
The cubic has minima at  and maxima at –
and maxima at –
The cubic has minima at – and maxima at
and maxima at
The cubic has minima at both  and-
and- 
The cubic has minima at both  and-
and- 
The differential equation of the family of circles with fixed radius 5 units and centre on the line y = 2 is
(x – 2)y′2 = 25 – (y – 2)2
(y – 2)y′2 = 25 – (y – 2)2
(y – 2)2y′2= 25 – (y – 2)2
(y – 2)2y′2= 25 – (y – 2)2
C.
(y – 2)2y′2= 25 – (y – 2)2
(x – h)2 + (y – 2)2 = 25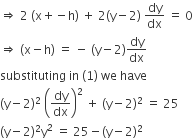
Let A be a square matrix all of whose entries are integers. Then which one of the following is true?
If det A = ± 1, then A–1 exists but all its entries are not necessarily integers
If detA ≠ ± 1, then A–1 exists and all its entries are non-integers
If detA = ± 1, then A–1 exists and all its entries are integers
If detA = ± 1, then A–1 exists and all its entries are integers
Let a, b, c be any real numbers. Suppose that there are real numbers x, y, z not all zero such that x = cy + bz, y = az + cx and z = bx + ay. Then a2 + b2 + c2 + 2abc is equal to
2
-1
0
0
The vector 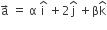 lies in the plane of the vectors
lies in the plane of the vectors  and bisects the angle between
and bisects the angle between  .Then which one of the following gives possible values of α and β?
.Then which one of the following gives possible values of α and β?
α = 2, β = 2
α = 1, β = 2
α = 2, β = 1
α = 2, β = 1
The line passing through the points (5, 1, a) and (3, b, 1) crosses the yz−plane at the point 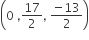 . Then
. Then
a = 2, b = 8
a = 4, b = 6
a = 6, b = 4
a = 6, b = 4
In a shop, there are five types of ice-creams available. A child buys six ice-creams.
Statement -1: The number of different ways the child can buy the six ice-creams is 10C5.
Statement -2: The number of different ways the child can buy the six ice-creams is equal to the number of different ways of arranging 6 A’s and 4 B’s in a row.
Statement −1 is false, Statement −2 is true
Statement −1 is true, Statement −2 is true, Statement −2 is a correct explanation for Statement −1
Statement −1 is true, Statement −2 is true; Statement −2 is not a correct explanation for Statement −1.
Statement −1 is true, Statement −2 is true; Statement −2 is not a correct explanation for Statement −1.
