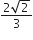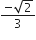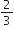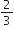Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe area (in sq units) of the region described by {x,y): y2 ≤ 2x and y ≥ 4x-1} is
7/32
5/64
15/64
15/64
Let y(x) be the solution of the differential equation 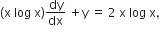 (x ≥1). Then, y (e) is equal to
(x ≥1). Then, y (e) is equal to
e
0
2
2
The number of points having both coordinates as integers that lie in the interior of the triangle with vertices (0,0), (0,41) and (41,0) is
901
861
820
820
Locus the image of the point (2,3) in the line (2x - 3y +4) + k (x-2y+3) = 0, k ε R is a
straight line parallel to X - axis
a straight line parallel to Y- axis
circle of radius 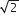
circle of radius 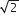
The area (in sq units) of the quadrilateral formed by the tangents at the end points of the latera recta to the ellipse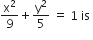
27/4
18
27/2
27/2
Let O be the vertex and Q be nay point on the parabola x2 = 8y. If the point P divides the line segment OQ internally in the ratio 1:3 then the locus of P is
x2= y
y2 =x
y2 =2x
y2 =2x
The distance of the point (1,0,2) from the point of intersection of the line 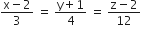 and the plane x-y +z = 16 is
and the plane x-y +z = 16 is

8


The equation of the plane containing the line 2x-5y +z = 3, x +y+4z = 5 and parallel to the plane x +3y +6z =1 is
2x + 6y + 12z = 13
x+3y+6z = -7
x+3y +6z = 7
x+3y +6z = 7
C.
x+3y +6z = 7
Let equation of plane containing the lines 2x- 5y +z = 3 and x+y+4z = 5 be
(2x-5y+z-3) + λ(x+y+4z-5) = 0
⇒ (2+λ)x + (λ-5)y + (4λ + 1)z -3 -5λ =0... (i)
This plane is parallel to the plane x +3y +6z = 1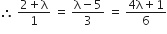
On taking first two equalities, we get
6λ -30 = 3 + 12λ
-6λ = 33
λ = - 11/2
So, the equation of required plane is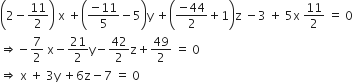
Let, a, b and c be three non-zero vectors such that no two of them are collinear and 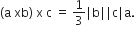 if θ is the angle between vectors b and c, then a value of sin θ is
if θ is the angle between vectors b and c, then a value of sin θ is