 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionspH of a saturated solution of Ba(OH)2 is 12. The value of solubility product Ksp of Ba(OH)2 is
3.3 x 10-7
5.0 x 10-7
4.0 x 10-6
4.0 x 10-6
In which of the following reactions, standard reaction entropy changes (ΔSo) is positive and standard Gibb's energy change (ΔGo) decreases sharply with increasing temperature?
C (graphite) +1/2 O2 (g) → CO (g)
CO (g) +1/2 (g) → CO2 (g)
Mg(s) +1/2O2 (g) → MgO (s)
Mg(s) +1/2O2 (g) → MgO (s)
Equimolar solutions of the following substances were prepared separately, which one of these will record the highest pH value?
BaCl2
AlCl3
LiCl
LiCl
50 mL of each gas A and of gas B takes 150 and 200 s respectively for effusing through a pin hole under the similar conditions. If molecular mass of gas B is 36, the molecular mass of gas A will be
96
128
20.2
20.2
C.
20.2
Given,
VA =VB = 50 mL
TA = 150 s
TB = 200 s
MB = 36
MA = ?
From Graham's law of effusion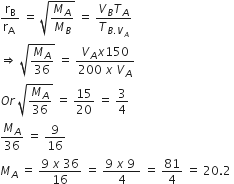
The correct set four quantum number for the valence electron of rubidium atom (z=37) is
5,1,1, +1/2
6,0,0,+1/2
5,0,0 +1/2
5,0,0 +1/2
Buffer solutions have constant acidity and alkalinity because
these give unionised acid or base on reaction with added acid or alkali
acids and alkalies in these solutions are shielded from attack by other ions.
they have a large excess of H+ or OH- ions
they have a large excess of H+ or OH- ions
The enthalpy of fusion of water is 1.435 Kcal/mol. The molar entropy change for the melting of ice of at 0o C is
10.52 cal/(mol K)
21.04 cal/(mol K)
5.260 cal/ (mol K)
5.260 cal/ (mol K)
Standard enthalpy of vaporisation ΔvapHθ for water for water at 100oC is 40.66 kJ mol-1. The internal energy of vaporisation of water at 100o C (in KJ mol-1) is
(Assume water vapour to behave like an ideal gas.)
+37.56
-43.76
+43.76
+43.76
