 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsWith respect to the conformers of ethane, which of the following statements is true?
Bond angle remains same but bond length changes
Bond angle changes but bond length remains same
Both bond angle and bond length change
Both bond angle and bond length change
Which of the following pairs of compounds is isoelectronic and isostructural?
BeCl2, XeF2
Tel2, XeF2
IBr2- , XeF
IBr2- , XeF
HgCl2 and I2 both when dissolved in water containing I– ions the pair of species formed is
HgI2 , I3-
Hgl2, I-
HgI43-, I3-
HgI43-, I3-
Which one is the wrong statement?
de-Broglie's wavelength is given by λ = h/mv,
where m = mass of the particle, v = group velocity of the particle
The uncertainty principle is 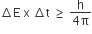
Half-filled and fully filled orbitals have greater stability due to greater exchange energy, greater symmetry and more balanced arrangement
Half-filled and fully filled orbitals have greater stability due to greater exchange energy, greater symmetry and more balanced arrangement
A gas is allowed to expand in a well-insulated container against a constant external pressure of 2.5 atm from an initial volume of 2.50 L to a final volume of 4.50 L. The change in internal energy ΔU of the gas in joules will be
1136.5 J
-500 J
-505 J
-505 J
The element Z = 114 has been discovered recently. It will belong to which of the following family group and electronic configuration?
Halogen family, [Rn] 5f14 6d10 7s2 7p5
Carbon family, [Rn] 5f14 6d10 7s2 7p2
Oxygen family,[Rn] 5f14 6d10 7s2 7p4
Oxygen family,[Rn] 5f14 6d10 7s2 7p4
Match the interhalogen compounds of column I with the geometry in column II and assign the correct code
| Column I | Column II |
| a) XX' | (i) T-shape |
|
b) XX3' |
(ii) Pentagonal |
|
c) XX'5 |
(iii) Linear |
| d) XX'7 | (iv) Square-pyramidal |
| (v) Tetrahedral |
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) |
| (iii) | (iv) | (i) | (ii) |
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) |
| (iii) | (i) | (iv | (ii) |
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) |
| (iv) | (v) | (iii) | (ii) |
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) |
| (iv) | (v) | (iii) | (ii) |
20-litre container at 400 K contains CO2(g) at pressure 0.4 atm and an excess of SrO (neglect the volume of solid SrO). The volume of the containers is now decreased by moving the movable piston fitted in the container. The maximum volume of the container, when pressure of CO2 attains its maximum value, will be
Given that: SrCO3 ⇌ SrO(s) + CO2(g) kp = 1.6 atm)
5 litre
10 litre
8 litre
8 litre
For a given reaction, ΔH = 35.5 kJ mol–1 and ΔS = 83.6 JK–1 mol–1. The reaction is spontaneous at (Assume that ΔH and ΔS do not vary with temperature)
T < 425 K
T > 425 K
All temperatures
All temperatures
The correct statement regarding electrophile is
Electrophile is a negatively charged species and can form a bond by accepting a pair of electrons from a nucleophile
Electrophile is a negatively charged species and can form a bond by accepting a pair of electrons from another electrophile
Electrophiles are generally neutral species and can form a bond by accepting a pair of electrons from a nucleophile
Electrophiles are generally neutral species and can form a bond by accepting a pair of electrons from a nucleophile