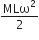Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsFor angles of projection of a projectile at angles (45° - θ) and (45° + θ), the horizontal ranges described by the projectile are in the ratio of
1:1
2:3
1:2
1:2
A body of mass 3 kg is under a constant force which causes a displacement s in metres in it, given by the relation 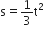 , where t is in s. Work done by the force in 2 s is:
, where t is in s. Work done by the force in 2 s is:


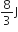
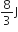
A particle moves along a straight line OX. At a time t (in seconds) the distance x (in metres) of the particle from O is given by
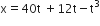
How long would the particle travel before coming to rest?
24m
40m
56m
56m
The velocity v of a particle at time t is given by 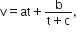 where a, b and c are constants, The dimensions of a, b and c are respectively:
where a, b and c are constants, The dimensions of a, b and c are respectively:




300 J of work is done in sliding a 2 kg block up an inclined plane of height 10 m. Taking =10 m/s2, work done against friction is
200 J
100 J
Zero
Zero
A 0.5 kg ball moving with a speed of 12 m/s strikes a hard wall at an angle of 30° with the wall. It is reflected with the same speed and at the same angle. If the ball is in contact with the wall for 0.25 s, the average force acting on the wall is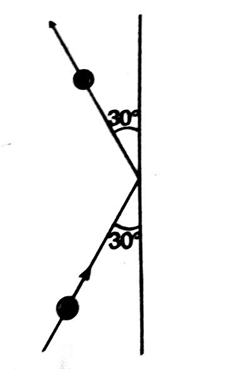
48 N
24 N
12 N
12 N
B.
24 N
The vector  represents the momentum of the object before the collision, and the vector
represents the momentum of the object before the collision, and the vector  that after the collision. The vector
that after the collision. The vector  represents the change in momentum of the object
represents the change in momentum of the object  .
. 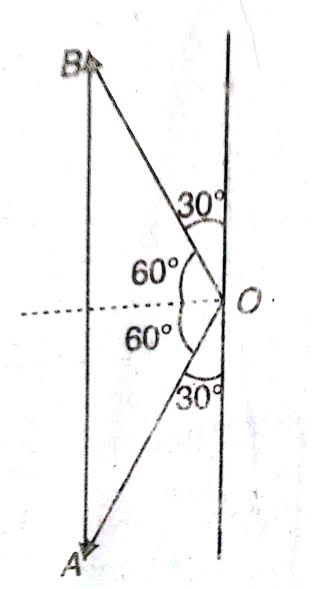
As the magnitudes of  are equal, the components of
are equal, the components of  along the wall are equal and in the same direction, while those perpendicular to the wall are equal and opposite. Thus, the change in momentum is due only to the change in direction of the perpendicular components.
along the wall are equal and in the same direction, while those perpendicular to the wall are equal and opposite. Thus, the change in momentum is due only to the change in direction of the perpendicular components.
Hence, 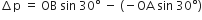

Its time rate will appear in the form of average force acting on the wall.
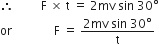
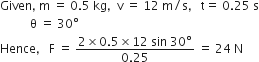
The moment of inertia of a uniform circular disc of radius R and mass M about an axis touching the disc at its diameter and normal to the disc is

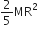
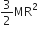
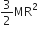
The earth is assumed to be a sphere of radius R. A platform is arranged at a height R from the surface of the earth. The escape velocity of a body from this platform is fve, where ve is its escape velocity from the surface of the earth. The value of f is
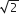

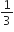
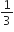
A car runs at aconstant speed on a circular track of radius 100 m, taking 62.8 s for every circular lap. The average velocity and average speed for each circular lap respectively is
0, 0
10 m/s, 10m/s
10 m/s, 10m/s
A tube of length L is filled completely with an incompressible liquid of mass M and closed at both the ends. The tube is then rotated in a horizontal plane about one of its ends with a uniform angular velocity ω. The force exerted by the liquid at the other end is