 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsA charged particle (charge q ) is moving n a circle of radius R with uniform speed v. The associated magnetic moment μ is given by:
qvR/2
qVR2
qVR2/2
qVR2/2
A steady current of 1.5 A flows through a copper voltameter for 10 min. If the electrochemical equivalent of copper is 30 x 10-5 g C-1, the mass of copper deposited on the electrode will be:
0.40 g
0.50 g
0.67 g
0.67 g
A hollow cylinder has to charge q coloumb within it. Φ is the electric flux in a unit of voltmeter associated with the curved surface B, the flux linked with the plane surface A in a unit of voltmeter will be:
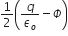
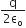
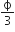
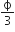
In mass spectrometer used for measuring the masses of ions, the are initially accelerated by an electric potential V and then made to describe semicircular paths of radius R using a magnetic field B. If V and B are kept constant, the ratio  will be proportional to:
will be proportional to:
1/R
1/R2
R2
R2
Three resistances P, Q, R each of 2 Ω and an unknown resistance S form the four arms of a Wheatstone's bridge circuit. When a resistance of 6 Ω is connected in parallel to S the bridge gets balanced. What is the value of S?
2 Ω
3 Ω
6 Ω
6 Ω
The electric and magnetic field of an electromagnetic wave are:
in phase and parallel to each other
in opposite phase and perpendicular to each other
in opposite phase and parallel to each other
in opposite phase and parallel to each other
Charge +q and -q are placed at points A and B respectively which are distance 2L apart, C is the midpoint between A and B.The work done in moving a charge + Q along the semicircle CED is: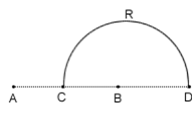




A common emitter amplifier has a voltage gain of 50, an input impedance of 100 Ω and an output impedance of 200 Ω. The power gain of the amplifier is:
500
1000
1250
1250
In radioactive decay process, the negatively charged emitted beta particles are:
the electrons present inside the nucleus
the electrons produced as a result of the decay of neutrons inside the nucleus
the electrons produced as a result of collisions between atoms
the electrons produced as a result of collisions between atoms
A small coin is resting on the bottom of a beaker filled with a liquid. A ray of light from the coin travels up to the surface of the liquid and moves along its surface (see figure). 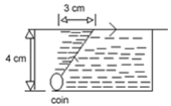
How fast is the light travelling in the liquid?
1.8 x 108 m/s
2.4 x 108 m/s
3.0 x 108 m/s
3.0 x 108 m/s
A.
1.8 x 108 m/s
The critical angle is the angle of incidence in the denser medium for which the angle of refraction in the rarer medium is 90o.
As shown in figure, a light ray from the coin will not emerge out of liquid, if i> C
Therefore, minimum radius R corresponds to
i= C. In ΔSAB,

