 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe interest on a certain sum of money is ₹ 22 and the discount on the same sum for the same time and at the same rate is ₹ 20, find the sum.
₹ 220
₹ 200
₹ 210
₹ 212
A retailer purchased radio sets at the rate of ₹ 400 each from a wholesaler. He raised the price by 30% and then allowed a discount of 8% on each set. His profit will be
19%
78.4%
22%
19.6%
A reduction in the price of apples enables a person to purchase 3 apples for ₹ 1 instead of ₹ 1.25. What is the per cent of reduction in price (approximately)?
20
25
30
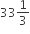
₹ 700 is divided among A, B, C in such a way that the ratio of the amounts of A and B is 2 : 3 and that of B and C is 4 : 5. Find the amounts (in ₹) each received, in the order A, B, C.
150, 250, 300
160, 240, 300
150, 250, 290
150, 240, 310
The ratio of monthly incomes of A, B is 6 : 5 and their monthly expenditure are in the ratio 4 : 3. If each of them saves ₹ 400 per month. Find the sum of their monthly incomes.
₹ 2300
₹ 2400
₹ 2200
₹ 2500
A and B have together three times what B and C have, while A, B, C together have ₹ 30 more than that of A. If B has 5 times that of C, then A has
₹ 60
₹ 65
₹ 75
₹ 45
A cricket player after playing 10 tests scored 100 runs in the 11th test. As a result, the average of his runs is increased by 5. The present age of runs is
45
40
50
55
A fruit seller buys some oranges at the rate of 4 for ₹ 10 and an equal number more at 5 for ₹ 10. He sells the whole lot at 9 for ₹ 20. What is his loss or gain per cent.
Loss per cent 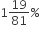
Gain per cent 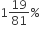
No loss or no profit
Loss per cent 2%
A.
Loss per cent 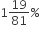
L.C.M. of 5 and 4 is 20.
So, let he bought 20 apples in both cases.
Case I,
4 apples bought for ₹ 10.
∴ 20 apples bought for ₹ (10 x 5) = ₹ 50. ...(i)
Case II,
5 apples bought for ₹ 10
∴ 20 apples bought for ₹ (10 x 4) = ₹ 40. ...(ii),
From equation (i) and (ii), we get
40 apples bought for ₹ (50 + 40) = ₹ 90.
∴ C.P. of one apple bought = ₹ (90/40) = ₹ 9/4
Case III,
9 apples sold for ₹ 20.
∴ S.P. of one apple = ₹ (20/9).
Since C.P. > S.P. (9/4 > 20/9), it means transaction resulted in loss.
Now, Required loss percent:
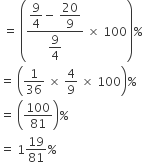
15 L of a mixture contains alcohol and water in the ratio 1 : 4. If 3 L of water is mixed in it, the percentage of alcohol in the new mixture will be
15
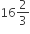
17
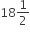
A man rides at the rate of 18 km/h but stops for 6 min to change horses at the end of every 7th km. The time that he will take to cover a distance of 90 km is
6 h
6 h 12 min
6 h 18 min
6 h 24 min
