Define the following terms and give their values for a normal eye:
(i) Range of normal vision.
(ii) Least distance of distinct vision.
(iii) Near point of the eye.
(iv) Far point of the eye.
(v) Power of accommodation.
(i) Range of normal vision: Due to accommodation property of the lens, a normal eye can clearly see the objects situated anywhere between infinity and 25 cm from it. At distance less than 25 cm, the ciliary muscles cannot bulge the eyelens any more, the object cannot be focussed on the retina and it appears blurred to the eye, as shown in Fig. The distance between infinity and 25 cm point is called the range of normal vision.
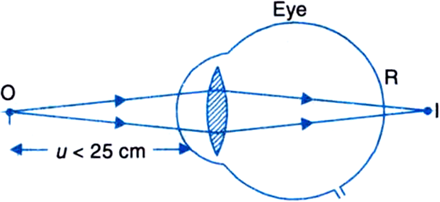
Fig. Object O within 25 cm from the eye is not focussed on retina and seen blurred
(ii) Least distance of distinct vision: The minimum distance from the eye, at which the eye can see the objects clearly and distinctly without any strain is called the least distance of distinct vision. It is denoted by the letter D. For a normal eye, its value is 25 cm.
(iii) Near point: The nearest point from the eye, at which an object can be seen clearly by the eye is called its near point. The near point of a normal eye is at a distance of 25 cm.
(iv) Far point: The farthest point from the eye, at which an object can be seen clearly by the eye is called the far point of the eye. For a normal eye, the far point is at infinity.
(v) Power of accommodation: The power of accommodation of the eye is the maximum variation of its power for focussing on near and far (distant) objects. For a normal eye, the power of accommodation is about four dioptres.
4023 Views

