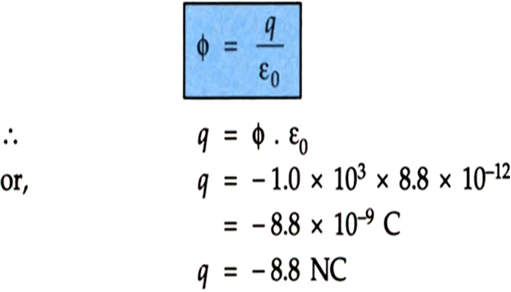A point charge causes an electric flux of -1.0 x 103 Nm2/C to pass through a spherical Gaussian surface of 10.0 cm radius centred on the charge. (a) If the radius of the Gaussian surface were doubled, how much flux would pass through the surface? (b) What is the value of the point charge?
Given, Φ = –1.0 x 103 Nm2/C
r1 = 0.1 m, r2 = 0.2 m
(a) Doubling the radius of Gaussian surface will not affect the electric flux since the charge enclosed is the same in the two cases. Thus, the flux will remain be the same i.e., –1.0 x 103 Nm2/C
(b)
417 Views