(a) State Ampere's circuital law, expressing it in the integral form.
(b) Two long coaxial insulated solenoids, S1 and S2 of equal lengths are wound one over the other as shown in the figure. A steady current 'I' flow thought the inner solenoid S1 to the other end B, which is connected to the outer solenoid S2 through which the same current 'I' flows in the opposite direction so as to come out at end A. If n1 and n2 are the number of turns per unit length, find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at a point
(i) Inside on the axis, and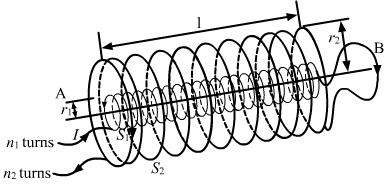
(a) Ampere’s circuital law states that the line integral of magnetic induction around a closed path in vacuum is equal to times the total current I threading the closed path. 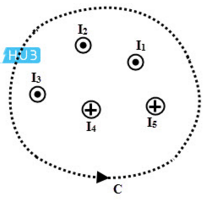
In the above illustration, the Ampere’s Circuital Law can be written as follows: ![]()
(b) (i) The magnetic field due to a current carrying solenoid:
where, n = number of turns per unit length
i = current through the solenoid.
From the fig, we can say that, the direction of magnetic field due to solenoid S1 will be in the upward direction and the magnetic field due to S2 will be in the downward direction using right hand screw rule.
Therefore, 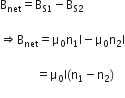
Net magnetic field is in the upward direction.
(ii) Since, there is no current which is flowing outside the solenoid, the magnetic field is zero.
