How does one explain, using de Broglie hypothesis, Bohr's second postulate of quantization of orbital angular momentum?
According to de-Broglie hypothesis, a stationary orbit is the one that contains an integral number of de-Broglie waves associated with the revolving electron.
Total distance covered by electron = Circumference of the orbit =
For the permissible orbit,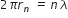 ... (1)
... (1)
Now, according to De-Broglie wavelength,
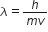
Now, putting this in equation (1), we have
 =
= 
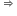 mvn rn =
mvn rn =  ; which is the required Bohr’s second postulate of quantization of orbital angular momentum.
; which is the required Bohr’s second postulate of quantization of orbital angular momentum.
