(a) Use Huygens' principle to show the propagation of a plane wavefront from a denser medium to a rarer medium. Hence find the ratio of the speeds of wavefront in the two media.
(b) (i) Why does an unpolarized light incident on a polaroid get linearly polarized ?
(ii) Derive the expression of Brewster's law when unpolarized light passing from a rarer to a denser medium gets polarized on reflection at the interface.
a) 
As seen in the fig. above let XY be a surface separating the two media ‘1’ and ‘2’. Let v1 and v2 be the speeds of waves in these media.
A plane wavefront AB in the first medium is incident obliquely on the boundary surface XY and its end A touches the surface at A at time t = 0 while the other end B reaches the surface at point B after time-interval t.
Here,  .
.
As the wavefront AB advances, it strikes the points between A and B’ of the boundary surface.
According to Huygens principle, secondary spherical wavelets emanate from these points, which travel with speed v1 in the first medium and speed v2 in the second medium.
Secondary wavelet starting from A, traverses a distance AA’ = v2t in second medium in time t. In the same time, the point of the wavefront traverses a distance in the first medium and reaches B’, from where the secondary wavelet starts.
So, BB' = v1 t and AA’ = v2t.
Assuming A as centre, we draw a spherical arc of radius AA’ (= v2t) and draw tangent B’A’ on this arc from B’. As the incident wavefront AB advances, the secondary wavelets start from points between A and B’, one after the other, and will touch A’B’ simultaneously.
According to Huygens principle A’B’ is the new position of wavefront AB in the second medium. Hence A’B’ will be the refracted wavefront.
Let the angle made by the incident wavefront be i and the angle made by the refracted wavefront A’B’ be r.

b)

Polarization of light is referred to as restricting the vibration of light in a perpendicular direction perpendicular to the direction of propagation of wave.
The vibration of particles of light which is parallel to the axis of crystal passes through the Polaroid on passing an unpolarized light. All other vibrations are absorbed and that is why the intensity of emerging light is reduced.
The plane of vibration here is ABCD, in which the vibrations of the polarized light are confined and the plane KLMN is called the plane of polarization. KLMN is perpendicular to the plane of vibration.
Reflected light is totally polarized, when unpolarized light is incident on the glass-air interface at the Brewster angle iB. This is known as Brewster’s law.
The reflected component OB and refracted component OC are mutually perpendicular to each other when light is incident at Brewster’s angle.
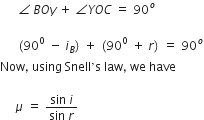
i = iB and r = (900 – iB)
Therefore, 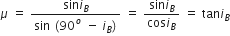 , is the expression for Brewster’s law.
, is the expression for Brewster’s law.
