We know that any point on x-axis is of the form P (x, 0).
Since, P (x, 0) is equidistant from A (2, -5) and B (-2, 9)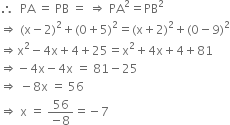
Hence, the required point is (-7, 0).
Let the required point be ‘P’ which is on the y-axis, so, its abscissa = 0 and ordinate (say) = y.
Thus co-ordinates of the point P are (0, y).
Let the given points be A(-5, -2) and B(3, 2).
It is given that: AP = BP
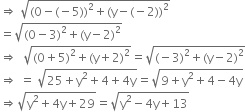
Squaring both side, we get
y2 + 4y + 29 = y2 - 4y + 13
⇒ 4y + 4y = 13 - 29
⇒ 8y = -16
⇒ y = -2
Therefore, the required point is (0, -2).
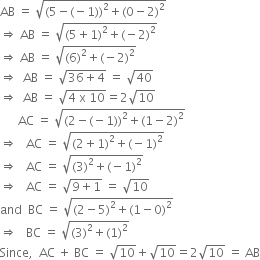
Let P(x, y), A(6, -1) and B(2, 3) be the given points
It is given that :AP = BP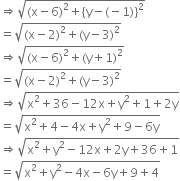
Squaring both side, we get
x2 + y2 - 12x + 2y + 36 + 1
= x2 + y2 -4x - 6y + 9 + 4
⇒ -8x + 8y + 24 = 0
⇒ -8(x - y - 3) = 0
⇒ x - y - 3 = 0 ⇒ x - y = 3.
