An object of height 4.0 em is placed at a distance of 30 cm from the optical centre ‘O’ of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. Draw a ray diagram to find the position and size of the image formed. Mark optical centre ‘O’ and principal focus ‘F’ on the diagram. Also find the approximate ratio of the size of the image to the size of the object.
Ray diagram:
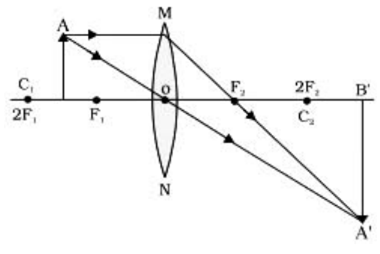
Here, focal length, f = 20 cm,
u = - 30 cm,
h0 = 4 cm
Using, lens formula,
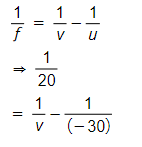
therefore, image distance, v = 60 cm
The image formed is real and inverted.
The ratio of the size of the image to the size of the object
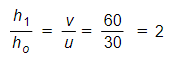
State the laws of refraction of light. Explain the term ‘absolute refractive index of a medium’ and write an expression to relate it with the speed of light in vacuum.
(1) The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal to the interface of two media at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
(2) For the light of a given colour and for a given pair of media, the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant.
This is also known as Snell's Law.
Mathematically it can be written as:
Here, μ is the refractive index of medium B with respect to medium A.
Refractive index of a medium with respect to the vacuum is known as the absolute refractive index.
What is meant by the power of a lens? Write its SI unit. A student uses a lens of focal length of 40 cm and another of –20 cm. Write the nature and power of each lens.
The power of lens is defined as the reciprocal of its length. It is denoted by using the letter P.
Unit of Power is Dioptre (D)
Focal length = 40 cm
Focal length = -20 cm
Convex lens P = 1/f = 100/40 = 2.5 D
Concave lens = P = 1/f = -100/20 = -5D
