What are the functions of the circulatory system?
The circulatory system performs the following functions :
(a) Transportation of gases : The gases like oxygen, carbon dioxide are transported from respiratory organs to every cell in the body. The oxygen is carried from lungs to body cells via heart and carbon dioxide from body cells to lungs.
(b) Transportation of nutrients : The different types of nutrients are transported to different cells.
(c) Transportation of waste products : The waste products like urea, uric acid, ammonia etc. are collected from different body tissues and poured into excretory organs.
(d) Transportation of water : Water and chemical substances are transported all over the body uniformly by blood.
(e) Transportation of hormones : The hormones secreted by the different endocrine glands are carried to their site of targets by blood.
Differentiate between an artery and a vein.
The walls T.S. artery and T.S. vein consist of three coats :
(a) Tunica externa : It is outermost layer and made up of connective tissue. The matrix has both white and yellow fibres arranged longitudinally.
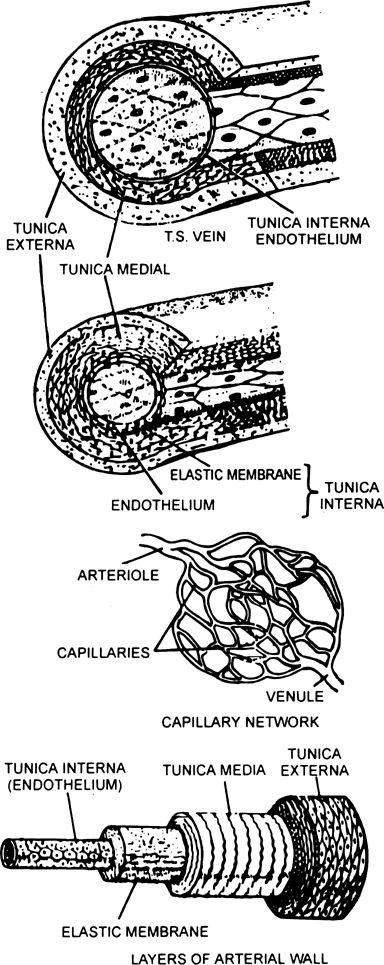
Fig. Structure of vein and artery and a capillary network
(b) Tunica media : It has a number of layers of smooth muscle fibres arranged in circles or in concentric rings. Tunica media is more developed in artery than in vein.
(c) Tunica interna : It has two parts, the outer layer which is more developed in artery and has yellow fibres. The other layer is endothelium. It has closely packed cells.
Describe double circulation.
Single blood circulation:In this type of circulation, blood only once comes
into heart.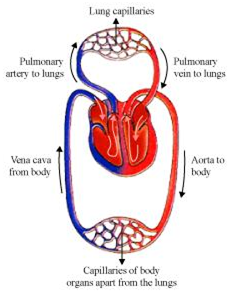
Fig. Single blood circulation in fishes
The impure blood from all parts of the body comes into heart and then circulated to gills. In gills, blood is purified and goes to dorsal aorta which supplies it to all parts of the body. It occurs in Scoliodon, Labeo etc. Such a heart which always gets deoxygenated blood for circulation is called venous heart.
Briefle describe the regulation of the cardiac activity.
The heart is myogenic that is it is auto regulated by specialised muscles (nodal tissue).
The cardiac acivity is regulated by the following:
i. A special neural centre in the medulla oblangata can moderate the cardiac function through autonomic nervous system (ANS).
ii. Neural signals through the sympathetic nerves (part of ANS) can increase the rate of heart beat, the strength of ventricular contraction and thereby the cardiac output.
iii. The parasympathetic neural signals decrease the rate of heart beat, speed of conduction of action potential and thereby the cardiac output.
iv. Adrenal medullary hormones can also increase the cardiac output.
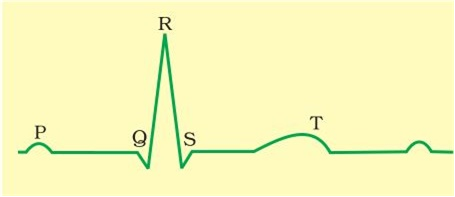
Draw a standard ECG and explain the different segments in it.