|
(c) Striped Muscles |
Unstriped Muscles |
Cardiac Muscles |
|
1. Present in limbs, neck tongue etc. |
Present in walls of the hollow organs. |
Present in myocardium of heart |
|
2. Myofibrils are very conspicuous in them. |
Inconspicuous in them. |
Myofibrils conspicuous in them. |
|
They have less blood supply. |
They have abundant blood supply. |
They have abundant blood supply. |
|
Voluntary. |
Involuntary. |
Involuntary. |
|
These are controlled by central nervous system. |
These are controlled by autonomic nervous system. |
These are controlled by brain and autonomic nervous system. |
|
Cylindrical in shape. |
These are spindle in shape. |
These are subcylinderical in shape. |
|
These are multinucleate. |
These are uninucleate. |
These are uninucleate. |
|
Oblique cross walls are absent. |
Oblique cross walls are absent. |
Oblique cross walls are present. |
|
Intercalated discs Absent |
Absent |
Present |
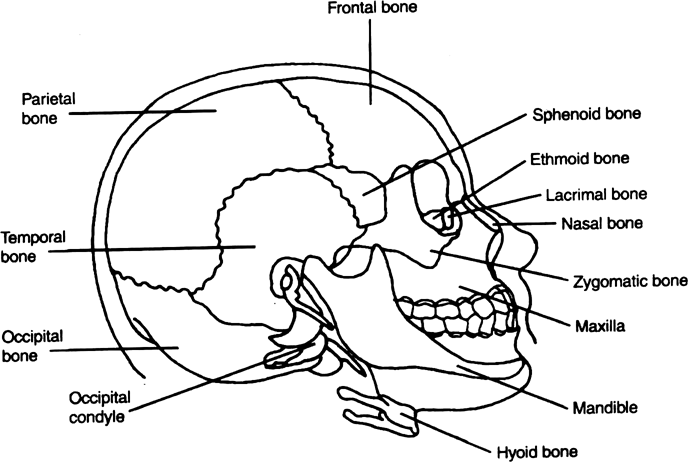
Fig. Human Skull
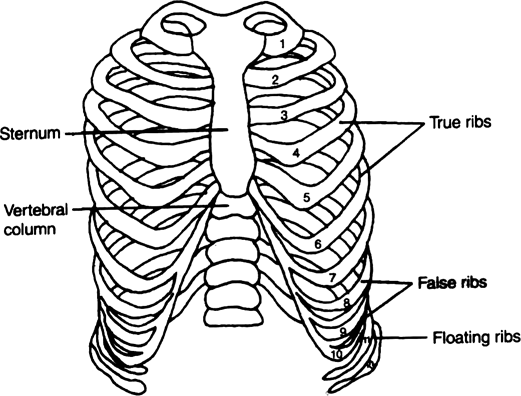
Fig. Ribs and Rib Cage
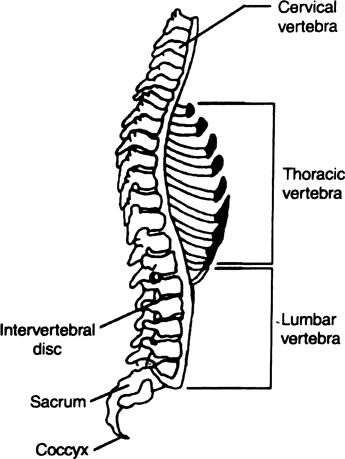
Vertebral Column
Osteoporosis :
Definition : It is reduction in bone tissue mass causing weakness of skeletal strength (G. osteon = bone, pros = pore, oisis = condition.)
Factors :
1. Excessive resorption of Ca+2 from bones : It results from excessive resorption of calcium and phosphorus from the bone, which leads to vertical compression or crush fracture of the vertebrae.
2. Menopause and Ca+2 absorption : Osteoporosis occurs in postmenopausal women and elderly men. It may result from defective intestinal calcium absorption.
3. Environmental factors : Possible environmental factors include smoking, excessive drinking and decreased exercise. Osteoporosis is more common in women than in men, and in old than middle aged persons.
4. Sex hormones : Imbalances of some hormones, thryocalcitonin, parathormone etc also cause osteoporosis.
5. Vitamin D : Deficiency of vitamin D causes osteoporosis.
Myosin filament : Each myosin (thick) filament is a polymerised monomeric proteins. The monomeric units are called Meromyosins. These constitute make one thick filament.
Each meromyosin has two important parts, a globular head with a short arm and a tail, the former being called the heavy meromyosin (HMM) and the latter, the light meromyosin (LMM). The HMM component, i.e.; the head and short arm projects outwards at regular
distance and angle from each other from the surface of a polymerised myosin filament and is known as cross arm. The globular head is an active ATPase enzyme and has binding sites for ATP and active sites for actin.
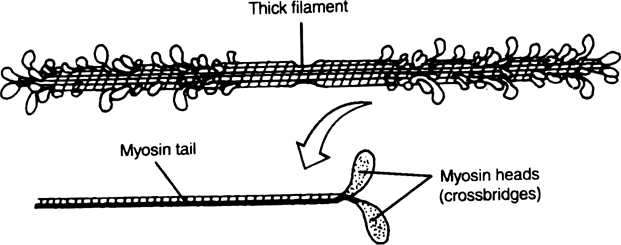
Thick filament (above) and a myosin molecule (below)
The movements and locomotion are neccessary among the animals because of following reasons :
1. Need for searching of shelter, food and water.
2. To escape from predators.
3. For shifting to favourable environment from an unfavourable one.
4. The movemenets of alimentary canal help in movement of food from one part of alimentary canal to next.
5. The ciliary movements help in the meovement of ova in fallopian tubes.
6. Movements of diaphragm and ribs help in breathing.
7. Movement of vocal cords help in the production of sound.
