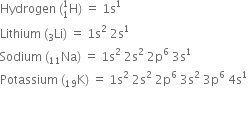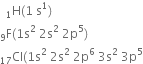Why does hydrogen occur in a diatomic form rather than in a monoatomic form under normal conditions?
A molecule of hydrogen is formed by the combination of two atoms of hydrogen with one electron each present in the 1s orbital. hydrogen (1s1) has one electron less than the stable inert gas configuration (He;1s2) and therefore it shares its single electron with an electron of another hydrogen atom to form a stable diatomic molecule. Thus two electrons are present in the hydrogen molecule and both will be accommodated in the molecular orbital of lowest energy. The bond order of H2 is +1. The positive value of bond order indicates that the H2 (diatomic) molecules are stable.
Name of isotopes of hydrogen: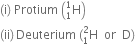

Describe the bulk preparation of hydrogen by an electrolytic method. What is the role of electrolyte in this process?
Or
How is dihydrogen manufactured by the electrolysis of water?
It is manufactured by the electrolysis of water containing a small amount of acid or alkali(electrolyte) using nickel plated iron as anode and iron as a cathode. The two electrodes are separated from each other by an asbestos diaphragm which prevents mixing of H2 and O2. On passing an electric current, water is decomposed into hydrogen and oxygen. Dihydrogen is collected at the cathode while oxygen is collected at the anode.
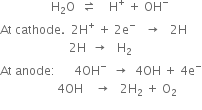
The role of electrolyte (acid) is to make water conducting.
How can the production of dihydrogen, obtained from 'coal gasification' be increased?