An earthquake generates both transverse (S) and longitudinal (P) sound waves in the earth. The speed of S waves is about 4.5 km/s and that of P waves is about 8.0 km/s. A seismograph records P and S waves from an earthquake. The first P wave arrives 4.0 min before the first S wave. The epicentre of the earthquake is located at a distance about
25 km
250 km
2500 km
5000 km
C.
2500 km
Velocity of the S wave is v1 = 4.5 km/s
The velocity of the P waves is v2 = 8.0 km/s
Let the time taken by the S and P waves to reach the seismograph be t1 and t2
It is given that
t1 t2 = 4 min
= 4 × 60 sec
t1 t2 = 240 sec .....(i)
Let the distance of the epicentre (km) be S. Then
S = v1t1 = v2t2
⇒ 4.5 × t1 8t2 = 0
⇒ t1 = t1 ....(ii)
Using (i) and (ii)
t1 t2 = 240
⇒ t1 = 240
⇒ t1 =
⇒ = 548.5 s
∴ S = v1t1
= 4.5 × 548.5
S = 2468.6
S ≈ 2500 km
A shell of mass m is at rest initially. It explodes into three fragments having masses in the ratio 2 : 2 : 1. The fragments having equal masses fly off along mutually perpendicular direction with speed v. What will be the speed of the third (lighter) fragment ?
We can represent in the form of a figure as
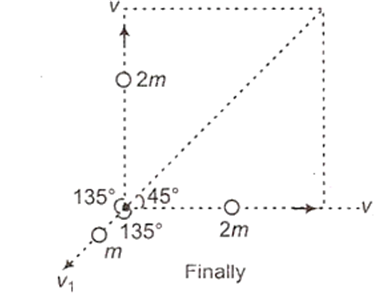
Now if we use the conservation of momentum we get
o = (2m) v cos 45° + (2m) v cos 45° + mv1
So, v1 = − 4 cos 45° v = − , thus the velocity of the third part has a magnitude equal to , this makes an angle of 135° with respect to either of the three masses.
A ball is thrown vertically upwards. Which of the following plots represents the speed-time graph of the ball during its flight if the air resistance is not ignored?
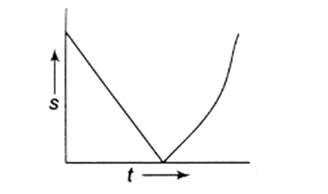
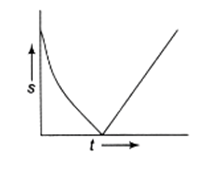
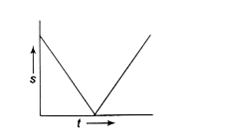
D.

During the upward motion, the speed of the body decreases and will be zero at the highest point (since the gravitational force acting downward), afterward, the body starts downward motion and its speed increases.
A cylinder of height h is filled with water and is kept on a block of height h/2. The level of water in the cylinder is kept constant. Four holes numbered 1,2, 3 and 4 are at the side of the cylinder and at heights 0, h/4, h/2 and 3h/4, respectively. When all four holes are opened together, the hole from which water will reach farthest distance on the plane PQ is the hole number
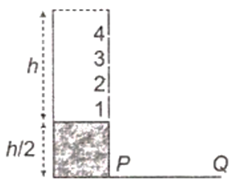
1
2
3
4
B.
2
Height of the cylinder from the level PQ is
To cover maximum distance along the plane PQ,
Height of the hole is
This height corresponds to hole (2).
