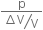
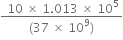Compute the bulk modulus of water from the following data: Initial volume = 100.0 litre, Pressure increase = 100.0 atm (1 atm = 1.013 × 105 Pa), Final volume = 100.5 litre. Compare the bulk modulus of water with that of air (at constant temperature). Explain in simple terms why the ratio is so large.
Initial volume, V1 = 100.0 l = 100.0 × 10 –3 m3
Final volume, V2 = 100.5 l = 100.5 ×10 –3
m3 Increase in volume, ΔV = V2 – V1 = 0.5 × 10–3 m3
Increase in pressure, Δp = 100.0 atm = 100 × 1.013 × 105 Pa

188 Views


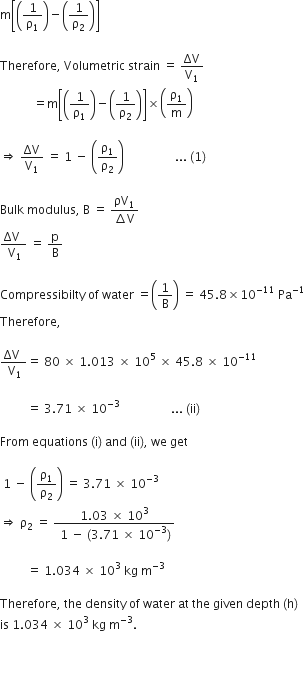
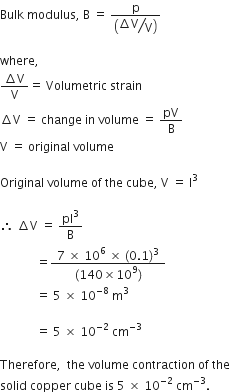
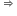 ρ = B × (∆V/V)
ρ = B × (∆V/V)