
Explain what happens when boric acid is heated.
Boric acid on heating forms a number of products depending upon the temperature. For example. 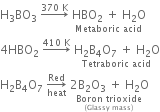
Describe the shapes of BF3 and  . Assign the hybridization of boron in these species ?
. Assign the hybridization of boron in these species ?
The shape of BF3 is a planar molecule in which the central boron atom is sp2 hybridised. A sp2 hybridised boron atom has a vacant p-orbital. 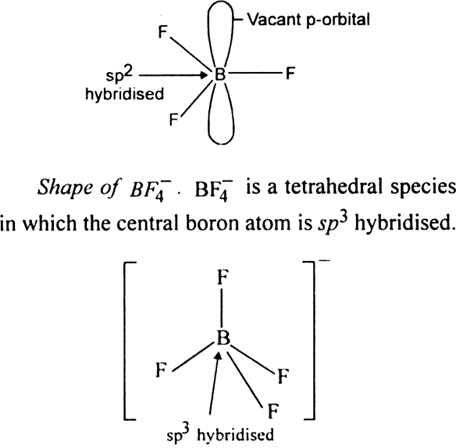
Discuss the pattern of variation in the oxidation states of B(Boron) to Tl(Thallium).
Or
What is inert pair effect? Illustrate it with reference to Boron family.
Inert pair effect: The inert pair effect represents the reluctance of the valence electrons to take part in the chemical combination due to their penetration in the nucleus of heavy elements.
B and Al do not exhibit inert pair effect due to the absence of d – or f-electrons. As a result, they show an oxidation state of +3 only due to the presence of two electrons in the s– and one electron in the p-orbital of the valence shell.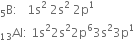
On the other hand, the elements from Ga to Tl contain only d and f-electrons and hence show oxidation states of +1 and +3 due to inert pair effect.
As we move down the group, the stability of +3 oxidation state decreases and that of +1 oxidation state increases. This means that as we move down the group, the tendency of the electrons of the valence shell to participate in bond formation decreases. In other words, ns2 electron pair in Ga, In and Tl tends to remain paired. This is called inert pair effect. Because of inert pair effect, only the electron of thallium takes parts in bonding with the atoms of the other elements. Thus, monovalent compounds of thallium are stable.
How can you explain the higher stability of BCl3 as compared to TlCl3?
This is because inert pair effect is maximum in thallium in which poor shielding of the s-electrons of the valence shell (6s2) by the 3d, -4d, -5d and 4f-electron occurs. As a result, only 6p1 electron participates in bond formation and thus the most stable oxidation state of Tl is +1 and not +3. Therefore, TlCl is stable while TlCl3 is unstable.
On the other hand, all the three valence electrons (2s22p1) of boron take part in the bond formation due to the absence of d–and f-electrons in B(no inert pair effects). Hence B shows an oxidation state of +3 and thus forms BCl3 easily. Thus BCl3 is more stable than TlCl3.
