Distribution of urban population and its growth rate is very uneven in the world. Describe.
(ii) An important point of world urbanisation is the great difference in the emerging trends between the developed and the developing regions of the world. In 1950, 20 of the world’s 30 largest metropolitan cities were located in developed countries, 11 in Europe and 6 in North America.
(iii) From a region of villages, Asia is fast becoming a region of cities and towns. Its urban population rose nearly five fold between 1950 and 1995 to 1.2 billion. There are 16 of the 30 largest cities of the world, in Asia. 45% of the world’s urban population lives in Asia. Almost all developing countries, are experiencing high rates of urbanisation. Karachi, in Pakistan, with 1.1 million population in 1950 is estimated to have 20.6 million in 2015. Likewise Cairo, Mumbai, Sao Paulo. Lagos etc. are projected to have populations in excess of 20 million by 2015.
Table: Continentwise Distribution of Million Cities
|
Continent |
Early 1950s |
Mid 1970s |
Mid 2000 |
|
Europe |
23 |
30 |
58 |
|
Asia |
32 |
69 |
206 |
|
North and Central |
|||
|
America |
16 |
36 |
79 |
|
South America |
8 |
17 |
43 |
|
Africa |
3 |
8 |
46 |
|
Australia |
2 |
2 |
6 |
|
World |
84 |
162 |
438 |
(iv) At present more then 36% of the urban population live in Asia and 16 out of 30 largest cities of the world are found in this continent. By 2015 out of world’s 358 cities 153 will be in Asia and out of 27 mega cities will be located in Asia.
Mention the three main rural settlement patterns based on structure found in different parts of the world.
Functions of Rural Settlement:
1. Majority of people are engaged in agriculture. All other facilities in village are related with agriculture. Some large villages have shops scattered in different mohallas where goods are sold for money.
2. In some villages settled along sea coasts, rivers the occupation is fishing and fisheries.
3. Mining is the main occupation of those people whose village are settled near mining centres.
4. The occupation in villages near forests is forestry, lumbering and gathering of medical herbs.
Main patterns of rural settlement:
(i) Rectangular Pattern or Cross-shaped Pattern: This is the most common type of rural settlement found in the villages of Gangetic plains of India. This pattern develops at the cross roads. Its shape is rectangular. The roads or lanes meet at right angles. The houses are built along the roads. This type is common in great plains of India.
(ii) Linear Pattern: This pattern takes an elongated linear shape and develops along the following sites:
(a) along either side of a road, (b) along a railway track, (c) along a river bank, (d) along the sea coast, (e) along the edge of a valley above flood level.
(iii) Triangular Pattern:
This pattern develops at the confluence of two rivers. One village develops on the land lying in between the two rivers. The expansion of village is restricted by the river. Sometimes a triangular pattern results in between two roads.
(iv) Star-like Pattern: This pattern develops along the roads spreading outward from the centre of the village.
(v) Circular Pattern: Houses built around the water bodies takes a circular shape.
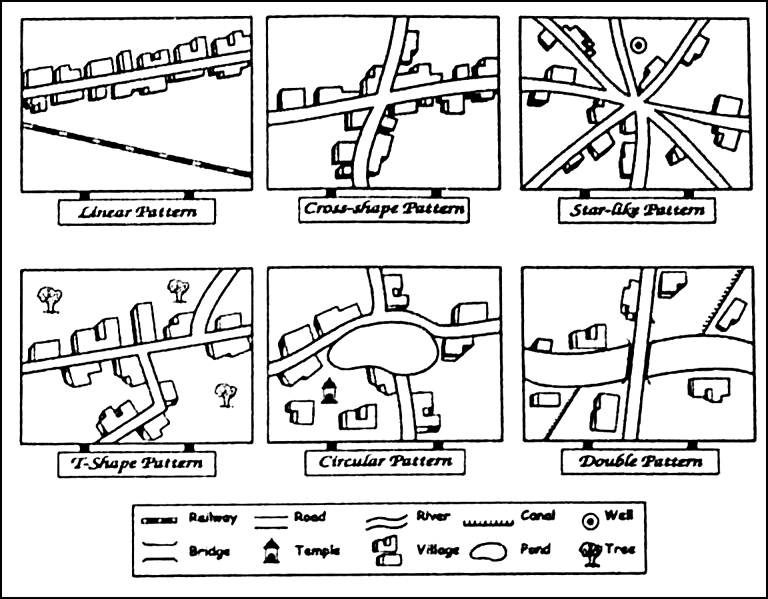
Fig.: Pattern of Rural Settlements
Examine any five environmental problems associated with urban settlements in the developing countries of the world.
What is a mega city? Make a list of mega cities of the world with country they are located with their population.
|
S.No. |
Name of the City |
Country |
Population (in million) |
|
1. |
Tokyo |
Japan |
34.2 |
|
2. |
Mexico City |
Mexico |
22.8 |
|
3. |
Seoul |
South Korea |
22.3 |
|
4. |
New York |
USA |
21.9 |
|
5. |
Sao Paulo |
Brazil |
20.2 |
|
6. |
Mumbai |
India |
19.9 |
|
7. |
Delhi |
India |
19.7 |
|
8. |
Shanghai |
China |
18.2 |
|
9. |
Los Angeles |
USA |
18.0 |
|
10. |
Osaka |
Japan |
16.8 |
|
11. |
Jakarta |
Indonesia |
16.6 |
|
12. |
Kolkata |
India |
15.7 |
|
13. |
Cairo |
Egypt |
15.6 |
|
14. |
Manila |
Philippines |
15.0 |
|
15. |
Karachi |
Pakistan |
14.3 |
|
16. |
Moscow |
Russia |
13.8 |
|
17. |
Buenos Aires |
Argentina |
13.5 |
|
18. |
Dhaka |
Bangladesh |
13.3 |
|
19. |
Rio De Janeiro |
Brazil |
12.2 |
|
20. |
Beijing |
China |
12.1 |
|
21. |
London |
G. Britain |
12.0 |
|
22. |
Tehran |
Iran |
11.9 |
|
23. |
Istanbul |
Turkey |
11.5 |
|
24. |
Lagos |
Nigeria |
11.1 |
|
25. |
Shenzhen |
China |
10.7 |
Distinguish between villages and towns.
|
Villages |
Towns |
|
1. Villages are the clusters of the house of the people who are mostly engaged in primary occupations such as agriculture, pastoral fishing and lumberings etc. |
1. Towns are the cluster of houses of the people who are mostly engaged in secondary and tertiary occupations such as business, industries and other services. |
|
2. They are comparatively of small size. |
2. They are bigger in size than the villages. |
|
3. They are administered by Gram Panchayat. |
3. They are administered either by municipality or by corporation or cantonment board. |
|
4. The houses are mostly made of mud and vegetation. The dwellings are mostly kachcha. |
4. The houses are mostly built of bricks or mortar. The houses are puckka and durable. |
|
5. Villages lack in modern facilities of life such as schools, transport, health and recreation etc. |
5. Towns enjoy the modern facilities of life. There are good education centres, health centres and recreation centres etc. |
|
6. They do not have market facility except once or two shops of daily use. |
6. There are good market centres. Villagers come here to sell their products and they buy the industrial goods. |
|
7. Villages are pollution free. |
7. Towns generally have polluted atmosphere due to the high density of population and industries etc. |
