Discuss the mechanical analysis of walking in details.
Mechanical analysis of walking can be studied in two fields
Stance phaser: Stance phase is the time when the foot is on the ground. It is considered that it consists maximum percentage of the walking cycle. For the part of stance phase, both the feet have contact with the ground for a period of time.
The stance phase is divided into five stages:
Heel strike: This stage begins when the feet first touch the ground & continues until the complete foot is on the ground i. e- early flat foot stage.
Early flat foot: The starting of this stage is that movement when the complete foot is on the ground and early flat foot stage occurs when the body’s center of gravity passes over the top of the foot. The center of gravity of the body is located approx. in the pelvic area of the lowest spine while walking. The main purpose of the stage is to allow the foot to act as a shock absorber.
Late flat foot: An athlete into late flat foot stage when his body’s center of gravity passes in front of the neutral position. This stage lasts when the heel lifts off the ground. During this stage, the foot needs to go from being a shock absorber to being a rigid level which can help to propel the body in forwarding direction.
Heel raise: This stage starts when the heel begins to leave the ground. The foot functions are a rigid lever to move the body in forwarding direction. During this stage of walking, the ground forces that go through the foot are very effective. Toe off this stage begins when the toes leave the ground completely. This stage continues until the beginning of swing phase.
Swing phase: It occurs when one foot is on the ground & the other one is in the air. Swing phase in walking is shorter than the stance phase. It is divided into three phases-
Initial swings: This phase sees the hip extending to 10 degrees 7 then going on to flexion and knee flexed to 40-60 degree & the ankle changing its position from the flexion to neutral.
Mid-swing: This phase sees the hip extending to 30 degrees, the knee flexion to 60 degrees & extended approx. to 30 degrees & ankle become dorsiflexed.
Terminal swing: This phase is the hip flexed till30 degree & the knee is locked extension & foot changes its position from dorsiflexed to neutral.
Mr Vinay is a physical education teacher in a govt. school and he was a renowned national level long jumper during his teenage. Mahesh is also a long jumper & his landing is improper. So he lost his position. Mahesh went to Mr Vinay to seek help Mr Vinay gave him proper scientific technique tip to follow correct body posture while landing & also motivated to utilize the same jump inconsistent practice. After the one year of training, Mahesh won a gold medal in the Inter-Zonal Athletic Meet.
I. What was the problem facing by Mahesh body?
II. State the qualities of Mr Vinay as a coach?
III. Explain the role of the coach in the life of a sportsman?
(i) He was facing problem in landing technique of Long Jump/ Mahesh was facing the problem of improper Landing in his long jump event so he didn’t win any medal in the athletic meet.
(ii) Mr Vinay has the following qualities.
1. Good motivate,
2, Dutifulness,
3. Knowledge of scientific techniques or mastering in skill,
4. Helping attitude,
5. Good coordination.
(iii) As a coach he can play in two different areas:
i. Information feedback, implementation in the respective field of skill.
ii. Suggest, refer, engage with field experts.
What are the different phases of the running cycle?
Running Is an essential part of living begins. Running is important in sports. A good runner will not only be able to defeat its opponents in running but would also be able to gain very good take off velocity that would help to make a higher or longer journey.
| Running style/phases | Sprinting | Fast Running | Jogging |
| Initial Contact | This phase sees the front of the foot of the sprinter making contact with the ground. Their heel might not or might touch the ground later depending on the person running technique. | This phase sees the middle of the foot or heel of the fast runner make contact with the ground. | This phase sees the full foot or heel of the jogger make contact with the ground. |
| Midstance | This phase is very quick and the sprinter's foot is usually in the same position as in the phase of initial contact. | This phase is very quick and the fast runner will spend this phase in midstance as he pushes through with his foot. | In comparison to sprinters and fast runners who use their feet and ankle to move into the next phase, jogger tends to move their center go gravity forward to the same. |
| Propulsion | This phase sees the hip of the sprinter extending back ready to propel him forward for takeoff. His arms simultaneously swing at full power to help him | The fast runner receives propulsion through the big toe with his hips extended back and knee slightly bent. | The jogger will receive propulsion through the big toe. But if the hip of the jogger is not fully extended back, then propulsion is received from other toes. only move a small amount. |
| swing | The non-supporting leg of sprinter swings high with the knee almost at the angle of 90 degrees. | The knee of the non-supporting leg of fast runner will be lifted although not as high as of a sprinter. | The knee of your non-supporting leg of jogger remains low and only slightly bent. |
What is Projectile? Explain the factor affecting projectile trajectory.
Projectile: - An object thrown into space either horizontally or an acute angle under the action under gravity is called a projectile. There are forces which act on a projectile – gravitational force and air resistance. Air resistance of an object varies greatly and it depends on the objects particular shape and the atmospheric conditions in which the object is released. The factor affecting projectile trajectory are mentioned below.
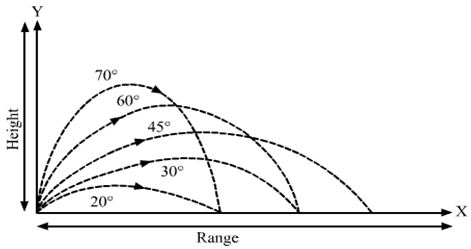
The angle of projection: - An object which is projected at different angles covers different distances. When it is projected or released at an angle of 30, making it a parabolic path and covers lesser distance. When it is projected at 60, it covers a distance of less than 30. When it is released at an angle of 45, makes a parabolic path and covers maximum distance. So the distance cover by an object( shout-put, hammer, javelin, discus etc. depends on the angle of release 0f projectile).
The height of release:- The higher the level of release, the greater distance is covered in flight, this is because the higher projectile is released. The longer it will be in the air. The horizontal component will be acting on the projectile for longer.
The speed of release (initial velocity):- The speed or velocity is directly related to the distance covered in the flight. The speed of the release depends on the initial vertical velocity an initial horizontal velocity. Having higher horizontal velocity will increase the length of the flight and therefore the distance covered. This would be an advantage in sports which requires primarily requires good distances in the long jump, sky jump etc.
Gravity:- Gravity acts on a body or object to give it mass. The greater the weight of an object, the greater the influence of gravity upon it. Gravity will effect a projectile as well as it will decrease the height, the projectile can obtain. For example, a cricket ball can be thrown at a greater distance in comparison to shot put.
Air resistance:- When a projectile moves through the air, it is slow down by an air resistance. Air resistance decreases the horizontal component of the projectile. The effect of air resistance is very small but it needs to be taken into consideration if you want to increase the horizontal component of the projectile. The factors are related to the amount of air resistance acting on a projectile- mass, the surface of the object, the surface of volume ratio.
Spin:- The amount & the direction of spin acting on a projectile will directly effect the distance while travelling.
