
Calculate the mole fraction of benzene in solution containing 30% by mass in carbon tetrachloride.
Molar mass of benzene,
Calculate (a) molality (b) molarity and (c) mole fraction of KI if the density of 20% (mass/mass) aqueous KI is 1.202 g mL-1.

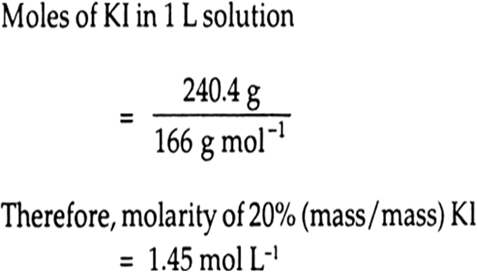
Molality (m) is defined as the number of moles of the solute per kilogram (kg) of the solvent and is expressed as:
solution;
Molarity (M) is defined as number of moles of solute dissolved in one litre (or one cubic decimetre) of solution.
(a) Mol. mass of
Moles of
Volume of solution = 4.3 L
Molarity,
(b) Number of moles present in 1000 ml of 0.5M H2SO4= 0.5 mol
therefore number of moles present in 30ml of 0.5M H2SO4=mol =0.015mol
therefore molarity =0.015/0.5L
thus molarity is 0.03M
