Describe the various types of motions observed in bodies.
Various types of motion as observed in bodies are:
1. Translatory motion: When a body moves as a whole along a straight or curved path, it is said to be in translatory motion.
Translatory motion is again of two types:
(i) Rectilinear motion: Here a body moves as a whole along a straight path.
For example, a train moving on straight rails has translatory rectilinear motion.
(ii) Curvilinear motion: In this case a body moves as a whole along a curved path.
For example, motion of a bicycle taking a turn along a curved path.
2. Rotatory motion: When a body rotates about a fixed point or axis, it exhibits a rotatory motion.
For example, motion of a flywheel about a shaft.
3. Vibratory or oscillatory motion: When a body moves to and fro about a mean position, the motion is said to be vibratory or oscillatory motion.
For example, the motion of the pendulum of a wall-clock.
4. Complex motion: When the motion of a body may be a combination of more than one types of motion, it is said to be a complex motion.
For example, a ball rolling down an inclined plane has both translatory and rotatory motions.
With the help of a suitable example, explain the terms distance and displacement.
Distance. It is the length of the actual path travelled by a body between its initial and final positions. In Fig. 8.2, suppose a body moves from position A to B through C. Then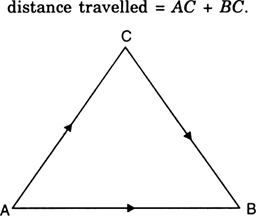
Distance is a scalar quantity because it has only magnitude and no direction. Distance covered is always positive or zero. Distance describes the total distance moved by an object.
Displacement. The change in the position of an object in a given direction is known as displacement. It is the shortest distance measured in the direction from the initial to the final position of the body. In Fig. 8.2,

As displacement has both magnitude and direction, so it is a vector quantity. It is measured in metre. If the measurement of displacement is expressed without direction, it is known as the magnitude of displacement. The magnitude of displacement is always less than or equal to the distance travelled.
Displacement may be positive, negative or zero. Displacement is used to locate the final position of an object with reference to its initial position at a given time.
Give some points of differences between distance and displacement.
Differences between distance and displacement are:
|
Distance |
Displacement |
|
1. Distance is the length of the actual path traversed by a body, irrespective of its direction of motion. |
1. Displacement is the shortest distance between the initial and final positions of a body in a given direction. |
|
2. Distance between two given points may be same or different for different paths chosen. |
2. Displacement between two given points is always same. |
|
3. It is a scalar quantity. |
3. It is a vector quantity. |
|
4. Distance covered is always positive. |
4. Displacement covered may be positive, negative or zero. |
What is meant by motion in a straight line ? Give some examples of such a motion.
When the position of a body changes with time, the body is said to be moving in a straight line.
Examples of motion in a straight line or rectilinear motion are:
(i) A bus moving on a straight road,
(ii) A train moving on a straight track,
(iii) A runner running along a straight track,
(iv) A ball moving along a straight path, and
(v) An object falling vertically downwards towards the surface of the earth.
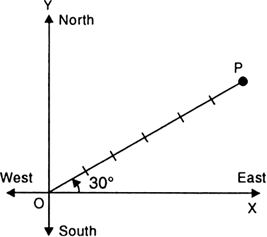
How can we specify the position of an object?
The position of an object can be specified by choosing :
(i) a fixed point called ‘origin’ or reference point, and
(ii) a fixed line passing through the origin, called reference axis.
So the position of an object can be fully described by knowing :
(i) its distance from origin O and
(ii) the angle θ which the line joining the origin O and the object makes with the reference axis.
In Fig. the position of an object located at point P is 6 m from the origin and 30° north of east.