 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe system of linear equations x+λy−z=0; λx−y−z=0; x+y−λz=0 has a non-trivial solution for
infinitely many values of λ.
exactly one value of λ.
exactly two values of λ.
exactly two values of λ.
D.
exactly two values of λ.
Given system of linear equations isÂ
x+λy−z=0;
λx−y−z=0;
x+y−λz=0Â
Note that, given system will have a non-trivial solution only if the determinant of the coefficient matrix is zero, ie.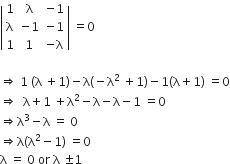
Hence, given system of linear equation has a non-trivial solution for exactly three values of λ.
For x ε R, f (x)=|log2−sinx| and g(x)=f(f(x)), then :
g is not differentiable at x=0
g'(0)=cos(log2)
g'(0)=-cos(log2)
g'(0)=-cos(log2)
Consider f(x) = tan-1 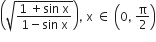 . A normal to y = f (x) at x = π/6 also passes through the point
. A normal to y = f (x) at x = π/6 also passes through the point
(0,0)
(0, 2Ï€/3)
(Ï€/6 ,0)
(Ï€/6 ,0)
A wire of length 2 units is cut into two parts which are bent respectively to form a square of side=x units and a circle of radius=r units. If the sum of the areas of the square and the circle so formed is minimum, then:
2x=(Ï€+4)r
(4−π)x=πr
x=2r
x=2r
If a curve y=f(x) passes through the point (1, −1) and satisfies the differential equation, y(1+xy) dx=x dy, then f(-1/2) is equal to
-2/5
-4/5
2/5
2/5
Let two fair six-faced dice A and B be thrown simultaneously. If E1 is the event that die A shows up four, E2 is the event that die B shows up two and E3 is the event that the sum of numbers on both dice is odd, then which of the following statements is NOT true?
E1 and E2 are independent
E2 and E3 are independent.
E1 and E3 are independent.
E1 and E3 are independent.
If 0≤x<2π, then the number of real values of x, which satisfy the equation cosx+cos2x+cos3x+cos4x=0, is :
3
5
7
7
