 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsTwo simple harmonic motions are represented by the equation y1 = 0.1 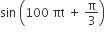 and y2 = 0.1 cosπt. The phase difference of the velocity of particle 1 w.r.t. the velocity of the particle 2 is
and y2 = 0.1 cosπt. The phase difference of the velocity of particle 1 w.r.t. the velocity of the particle 2 is
−π/6
π/3
−π/3
−π/3
A.
−π/6
Phase difference (φ) = 99πt + π/3 −π/2 at
t = 0 φ = −π/6
A heater coil is cut into two equal parts and only one part is now used in the heater. The heat generated will now be
doubled
four times
one fourth
one fourth
When two tuning forks (fork 1 and fork 2) are sounded simultaneously, 4 beats per second are heard. Now, some tape is attached on the prong of the fork 2. When the tuning forks are sounded again, 6 beats per seconds are heard. If the frequency of fork 1 is 200 Hz, then what was the original frequency of fork 2?
200 Hz
202 Hz
196 Hz
196 Hz
If a simple harmonic motion is represented by , its time period is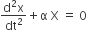 its time period
its time period
2π/α
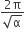
2πα
2πα
The bob of a simple pendulum is a spherical hollow ball filled with water. A plugged hole near the bottom of the oscillation bob gets suddenly unplugged. During observation, till water is coming out, the time period of oscillation would
first increase and then decrease to the original value.
first decreased then increase to the original value.
remain unchanged.
remain unchanged.
An observer moves towards a stationary source of the sound, with a velocity one-fifth of the velocity of sound. What is the percentage increase in the apparent frequency?
0
0.5%
5%
5%
A moving coil galvanometer has 150 equal divisions. Its current sensitivity is 10 divisions per milliampere and voltage sensitivity is 2 divisions per millivolt. In order that each division reads 1 volt, the resistance in ohms needed to be connected in series with the coil will be
103
105
99995
99995
Two voltameters one of copper and another of silver, are joined in parallel. When a total charge q flows through the voltameters, equal amount of metals are deposited. If the electrochemical equivalents of copper and silver are z1 and z2 respectively the charge which flows through the silver voltameter is
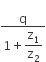
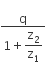
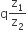
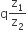
In the circuit, the galvanometer G shows zero deflection. If the batteries A and B have negligible internal resistance, the value of the resistor R will be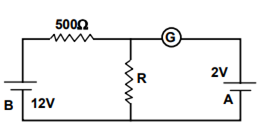
200Ω
100Ω
500 Ω
500 Ω
A fully charged capacitor has a capacitance ‘C’ it is discharged through a small coil of resistance wire embedded in a thermally insulated block of specific heat capacity ‘s’ and mass ‘m’. If the temperature of the block is raised by ‘∆T’. The potential difference V across the capacitance




