 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsA body under the action of a force, acquires an acceleration of 1 ms-2. The mass of this body must be
acquires an acceleration of 1 ms-2. The mass of this body must be

20 kg
10 kg
10 kg
D.
10 kg
According to Newton's second law of motion, force = mass x acceleration.
Here, 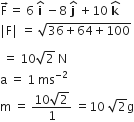
A bar magnet having a magnetic moment of 2 x 104 JT-1 is free to rotate in a horizontal plane. A horizontal magnetic field B = 6 x 10-4 T exists in the space. The work is done in taking the magnet slowly from a direction parallel to the field to a direction 60o from the field is
0.6 J
12 J
6 J
6 J
If  is the force acting on a particle having position vector
is the force acting on a particle having position vector  be the the torque of this force about the origin, then
be the the torque of this force about the origin, then




A wave in a string has an amplitude of 2 cm. The wave travels in the +ve direction of x -axis with a speed of 128 ms-1 and it is noted that 5 complete waves fit in 4 m length of the string. The equation describing the wave is
y = (0.02) m sin (7.85 x +1005t)
y = (0.02) m sin (15.7 x -2010t)
y = (0.02) m sin (15.7 x + 2010t)
y = (0.02) m sin (15.7 x + 2010t)
A simple pendulum performs simple harmonic motion about x = 0 with an amplitude a and time period T. the speed of the pendulum at x = a/2 will be

πa / T
3π2a / T
3π2a / T
A block body t 227o C radiates heat at the rate of 7 cal cm-2 s-1. At a temperature of 727o C, the rate of heat radiated in the same units will be
60
50
112
112
The internal energy change in a system that has absorbed 2 Kcal of heat and done 500 J of work is
8900 J
6400 J
5400 J
5400 J
An engine pumps water continuously through a hose. Water leaves the hose with a velocity v and m is the mass per unit length of the water jet. What is the rate at which kinetic energy is imparted to water?
mv3 /2
mv3
mv2/2
mv2/2
Which one of the following equations of motion represents simple harmonic motion?
Acceleration = -ko x +k1x2
Acceleration =-k(x+a)
Acceleration = k (x+a)
Acceleration = k (x+a)
In a thermodynamic process which of the following statements is not true?
In an adiabatic process, the system is insulated from the surroundings
In an isochoric process pressure remains constant
In an isothermal process, the temperature remains constant
In an isothermal process, the temperature remains constant
