 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsWhat is the minimum velocity with which a body of mass m must enter a vertical loop of radius R so that it can complete the loop?




C.

The question is illustrated in the figure below,
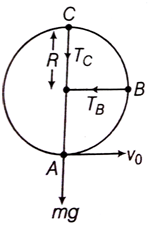 Let, the tension at point A be TA.
Let, the tension at point A be TA.
Using Newton's second law, we have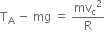
Energy at point A = 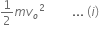
Energy at point C is,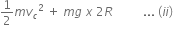
At point C, using Newton's second law,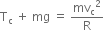
In order to complete a loop, Tc 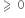
So,
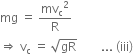
From equation (i) and (ii)
Using the principle of conservation of energy,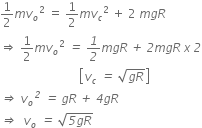
A particle of mass 10 g moves along a circle of radius 6.4 cm with a constant tangential acceleration. What is the magnitude of this acceleration, if the kinetic energy of the particle becomes equal to 8 x 10-4 J by the end of the second revolution after the beginning of the motion?
0.15 m/s2
0.18 m/s2
0.2 m/s2
0.2 m/s2
Two non-mixing liquids of densities 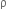 and n
and n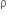 (n >1) are put in a container. The height of each liquid is h. a solid cylinder of length L and density d is put in this container. The cylinder floats with its axis vertical and length pL (p<1) in the denser liquid. The density d is equal to,
(n >1) are put in a container. The height of each liquid is h. a solid cylinder of length L and density d is put in this container. The cylinder floats with its axis vertical and length pL (p<1) in the denser liquid. The density d is equal to,
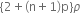

{1+(n-1)p}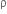
{1+(n-1)p}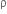
Out of the following options which one can be used to produce a propagating electromagnetic wave?
A stationary charge
A chargeless particle
An accelerating charge
An accelerating charge
The charge following through a resistance R varies with time t as Q = at - bt2, where a and b are positive constants. The total heat produced in R is,
a3R/3b
a3R/2b
a3R/b
a3R/b
Coefficient of linear expansion of brass and steel rods are 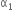 and
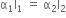
and  . Lengths of brass and steel rods are l1 and l2 respectively. If (I2 - I1) is maintained same at all temperatures, which one of the following relations holds good?
. Lengths of brass and steel rods are l1 and l2 respectively. If (I2 - I1) is maintained same at all temperatures, which one of the following relations holds good?



An air column, closed at one end and open at the other, resonates with a tuning fork when the smallest length of the column is 50 cm. The next larger length of the column resonating with the same tuning fork is,
100 cm
150 cm
200 cm
200 cm
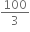
The molecules of a given mass of a gas have r.m.s. velocity of 200 m/s at 27o C and 1.0 x 105 Nm-2 pressure. When the temperature and pressure of the gas are respectively, 127o C and 0.05 x 105 Nm-2, the RMS velocity of its molecules in m/s is,



A gas is compressed isothermally to half its initial volume. The same gas is compressed separately through an adiabatic process until its volume is again reduced its half. Then,
compressing the gas through adiabatic process will require more work to b done
compressing the gas through isothermally or adiabatically will require the same amount of work.
which of the case (whether compression through isohermal or through adiabatic process) requires more work will depend upon the atomicity of the gas.
which of the case (whether compression through isohermal or through adiabatic process) requires more work will depend upon the atomicity of the gas.
A piece of ice falls from a height h so that it melts completely. Only one-quarter of the heat produced is absorbed by the ice and all energy of ice gets converted into heat during its fall. The value of h is [Latent heat of ice is 3.4 x 105 J/kg and g =10 N/kg]
544 km
136 km
68 km
68 km
