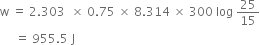Define thermodynamics.
The branch of science which deals with the study of different forms of energy and the quantitative relationships between them is known as thermodynamics.
(a) What are Exergonic and Endergonic reactions?
(b) Given that the standard heat of formation of NH3(g) as represented by the equation![]()
is – 46.191 kJ. The standard entropies of N2(g), H2(g) and NH3(g) are 191.62, 130.12 and 193.3 JK–1 mol–1 respectively. Calculate the standard free energy of formation (∆G0) for NH3. Is the reaction feasible?
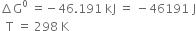
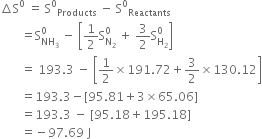
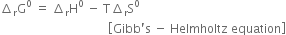
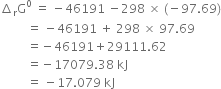
(i) What are the limitations of criterion for randomness?
(ii) Calculate the standard free energy of formation of ![]() The free change for the reaction.
The free change for the reaction.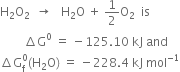

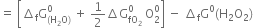
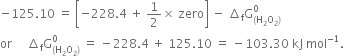
What do you understand by the terms: the system and surroundings?
A system in thermodynamics refers to that part of the universe in which observations are made and remaining universe constitutes the surrounding. The surroundings include everything other than the system. System and the surroundings together constitute the universe.
(i) Define first and the second law of thermodynamics in the combined form.
(ii)
(a) Write an expression for the entropy change of an ideal gas for isothermal change.
(b) Write an expression for entropy change for an ideal gas for isobaric change.
(iii) Calculate the maximum work obtained when 0.75 ml of an ideal gas expands isothermally and reversibly at 27°C from a volume of 15L to 25L.
(i) The energy of the universe is constant but the entropy of the universe is continuously increasing and tends to a maximum.
(ii)
(a)
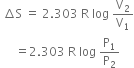
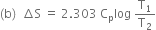
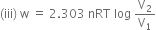
Substituting the values, we have,