 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe heats of combustion of carbon and carbon monoxide are −393.5 and −283.5 kJ mol−1, respectively. The heat of formation (in kJ) of carbon monoxide per mole is:
676.5
-676.5
-110.5
-110.5
The following reaction is performed at 298 K
2NO(g) + O2 (g) ⇌ 2NO2 (g)
The standard free energy of formation of NO (g) is 86.6 kJ/mol at 298 K. What is the standard free energy of formation of NO2 (g) at 298 K? (KP = 1.6 x 1012)
R (298) In (1.6 x 1012)-86600
86600 + R (298) In (1.6 x 1012)
86600 - In(1.6 x 1012)/R(298)
86600 - In(1.6 x 1012)/R(298)
The standard Gibbs energy change at 300 K for the reaction, 2A ⇌ B +C is 2494.2J at a given time, the composition of the reaction mixture is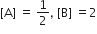 and
and 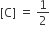 , The reaction proceeds in the [R= 8.314 JK/mol, e = 2.718]
, The reaction proceeds in the [R= 8.314 JK/mol, e = 2.718]
forward direction because Q>Kc
reverse direction because Q>Kc
forward direction because Q < Kc
forward direction because Q < Kc
For the complete combustion of ethanol, C2H5OH (l) + 3O2 (g) → 2CO2 (g) + 3H2O (l), the amount of heat produced as measured in a bomb calorimeter, is 1364.47 kJ mol-1 at 25oC. Assuming ideality the enthalpy of combustion, ∆CH, for the reaction will be (R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1)
-1366.95 kJ mol-1
-1361.95 kJ mol-1
-1460.50 kJ mol-1
-1460.50 kJ mol-1
A piston filled with 0.04 mol of an ideal gas expands reversibly from 50.0 mL to 375 mL at a constant temperature of 37.00C. As it does so, it absorbs 208J of heat. The values of q and w for the process will be:(R = 8.314 J/mol K) ( ln 7.5 = 2.01)
q =+208J, W = - 208 J
q =-208 J, W =-208 J
q=-208J, W = +208 J
q=-208J, W = +208 J
The standard reduction potentials for Zn2+/ Zn, Ni2+/ Ni, and F2+/ Fe are –0.76, –0.23 and –0.44 V respectively. The reaction X + Y2+ → X 2+ + Y will be spontaneous when
X = Ni, Y = Fe
X = Ni, Y = Zn
X =Fe, Y= Zn
X =Fe, Y= Zn
The entropy change involved in the isothermal reversible expansion of 2 moles of an ideal gas from a volume of 10 dm3 to a volume of 100 dm3 at 27°C is
38.3 J mol-1 K-1
35.8 J mol-1 K-1
32.3 J mol-1 K-1
32.3 J mol-1 K-1
The standard enthalpy of formation of NH3 is– 46.0 kJmol–1. If the enthalpy of formation of H2 from its atoms is – 436 kJ mol–1 and that of N2 is – 712 kJ mol–1,the average bond enthalpy of N – H bond is NH3 is
-964 kJ mol-1
+352 kJ mol-1
+1056 kJ mol-1
+1056 kJ mol-1
The energy required to break one mole of Cl— Cl bonds in Cl2 is 242 kJ mol–. The longest wavelength of light capable of breaking a single Cl — Cl bond is
(c= 3 x 108 ms–1and NA = 6.02 x 1023 mol–1)
594 nm
640 nm
700 nm
700 nm
