 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type(a) Identify (A) and (B) illustrations in the following:
i. 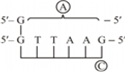
ii. 
(b) Write the term given to (A) and (C) and why?
(c) Expand PCR. Mention its importance in biotechnology.
(a) A represents - Sticky end.
B represents - Foreign DNA insert.
(b) The term used for A is Sticky ends, it is called so because they form hydrogen bonds with their complementary cut counterparts. Their stickiness of the ends facilitates the action of the enzyme DNA ligase.
C are called the palindromic nucleotide sequence. These are named so because the sequence of base pairs reads same on the two strands when orientation of reading is kept the same
(c) PCR stands for Polymerase Chain Reaction. PCR is a technique used to synthesize multiple copies of the gene (or DNA) of interest in vitro using two sets of primers (small chemically synthesized oligonucleotides that are complementary to the regions of DNA) and the enzyme DNA polymerase. It is extensively used in the process of gene manipulation.
Rearrange the following in the current sequences to accomplish an important biotechnological reaction :
(a) In vitro synthesis of region of DNA of interest
(b) Chemically synthesized oligonucleotides
(c) Enzyme DNA-polymerase
(d) Complementary region of DNA
(e) Genomic DNA template
(f) Nucleotides provided
(g) Primers
(h) Thermostable DNA-polymerase (from Thermus aquaticus)
(i) Denaturation of ds-DNA
Why is it not possible for an alien DNA to become part of a chromosome anywhere along its length and replicate normally?
Name the enzymes that are used for the isolation of DNA from bacterial and fungal cells for recombinant DNA technology.
Name and describe the technique that helps in separating the DNA fragments formed by the use of restriction endonuclease.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) Describe the various steps of Griffith’s experiment that led to the conclusion of the ‘Transforming Principle’.
(b) How did the chemical nature of the ‘Transforming Principle’ get established?
