 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type(a) Identify (A) and (B) illustrations in the following:
i. 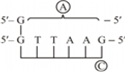
ii. 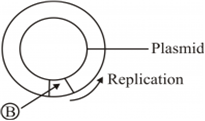
(b) Write the term given to (A) and (C) and why?
(c) Expand PCR. Mention its importance in biotechnology.
Rearrange the following in the current sequences to accomplish an important biotechnological reaction :
(a) In vitro synthesis of region of DNA of interest
(b) Chemically synthesized oligonucleotides
(c) Enzyme DNA-polymerase
(d) Complementary region of DNA
(e) Genomic DNA template
(f) Nucleotides provided
(g) Primers
(h) Thermostable DNA-polymerase (from Thermus aquaticus)
(i) Denaturation of ds-DNA
Why is it not possible for an alien DNA to become part of a chromosome anywhere along its length and replicate normally?
Name the enzymes that are used for the isolation of DNA from bacterial and fungal cells for recombinant DNA technology.
Name and describe the technique that helps in separating the DNA fragments formed by the use of restriction endonuclease.
Gel electrophoresis is the technique that is used to separate the DNA fragments formed by the use of restriction endonucleases.
In this technique the DNA fragments are separated on the basis of the charge , since the DNA molecule is negatively charged they are forced to move towards the anode under an electric field applied through the medium or the matrix in which the DNA is loaded. The matrix used is generally made of agarose.
i. The DNA fragments cut by the restriction enzymes, separate according to their size through the sieving effect provided by the agarose gel.
ii. The smaller the DNA fragment the faster it travels. Smaller segments travel more distance than larger DNA molecules.
iii. The DNA which is usually stained with the EtBr dye or ethidium bromide, is visualized under UV light. The DNA appear as orange bands. 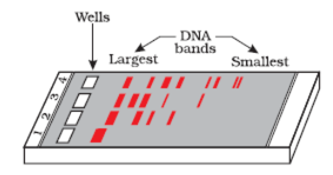
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) Describe the various steps of Griffith’s experiment that led to the conclusion of the ‘Transforming Principle’.
(b) How did the chemical nature of the ‘Transforming Principle’ get established?
