 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeDefine : Embolus, thrombus, thrombophilia, vasodilation, thrombocytopenia, acapnia, pulse pressure.
Define blood clotting and describe the mechanism of blood clotting.
Blood clotting : It is the natural device to check bleeding.
Mechanism : It involves two steps :
1. Vasocontraction : At the point of injury, the blood vessels contract and flow of blood is reduced.
2. Formation of clot :
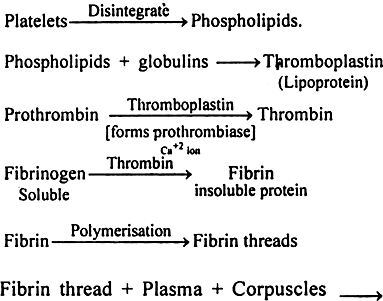
(i) Formation of thromboplastin : At the point of injury the platelets disintegrate to form phospholipids. The phospholipids and globulins combine to form thromboplastin, which is an antiheparin.
(ii) Formation of thrombin : The thromboplastin synthesises prothrombiase. The prothrombiase and Ca+2 ions convert prothrombin into thrombin.
(ii) Synthesis of fibrin threads : The thrombin converts fibrinogens (soluble protein) into fibrin (insoluble protein). The fibrin undergoes polymerisation to form fibrin threads.
(iv) Clot : The fibrin threads form a network and blood corpuscles cannot pass out. Thus, a clot is formed. The clot when gets dried becomes dark brown. The colourless plasma passes out from dark brown clot. It is called blood serum. If clotting of the blood occurs in the body, then clot is called thrombus and process is called thrombosis.
The thrombus formed in the heart and blood vessels of brain may prove to be fatal.
If blood does not clot when injury has occured, then the disease is called haemophilia. It is due to the sex linked gene present on X-chromosome.
Clot.
Name the components of the formed elements in the blood and mention one major function of each of them.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWhat is the significance of atrio-ventricular node and atrio-ventricular bundle in the functioning of heart?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type