 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWhat is the significance of meiosis?
Meiosis is the reduction division the reduction in the amount of genetic material.
Significance of meiosis
1. Meiosis maintains the chromosome number from generation to generation. It reduces the chromosome number to half so that the process of fertilisation can restore the original number in the zygote.
2. It has an evolutionary importance as it allows variations to occur. The process of cross-over and the random distribution of homologous chromosomes between daughter cells result in variation in the genetic make-up of the cells. Variations play an important role in evolution.
3. Chromosomal mutations are brought about by the introduction of certain inheritable changes which may be advantageous for an individual.
 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsMicrotubules are the constituent of
spindle fibres, centrioles and cilia
centrioles, spindle fibres and chromatin
centrosome, nucleosomes and centrioles
centrosome, nucleosomes and centrioles
A cell at telophase stage is observed by a student in a plant brought from the field. He tells his teacher that this cell is not like other cells at telophase stage. there is no formation of cell plate and thus the cell is containing more number of chromosomes as compares to other dividing cells. This would result in
polyploidy
somaclonal variation
polyteny
polyteny
Which of the following is not a characteristic feature during mitosis in somatic cells?
Disappearance of nucleolus
Chromosome movement
Synapsis
Synapsis
Spindle fibres attach on to
kinetochore of the chromosome
centrosome of the chromosome
kinetosome of the chromosome
kinetosome of the chromosome
The complex formed by a pair of synapsed homologous chromosomes is called
equatorial plate
kinetochore
bivalent
bivalent
The cell -mediated immunity inside the human body is carried out by
T- lymphocytes
B - lymphocytes
thrombocytes
thrombocytes
A stage in cell division is shown in the figure. Select the answer which gives correct identification of the stage with its characteristics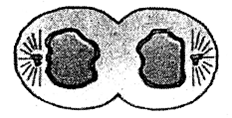
|
Telophase |
Nuclear envelope reforms, Golgi complex reforms |
|
Late anaphase |
Chromosomes move away from equatorial plate, Golgi complex not present |
|
Cytokinesis |
Cell plate formed, Mitochondria distributed between two daughter cells |
|
Cytokinesis |
Cell plate formed, Mitochondria distributed between two daughter cells |
