 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
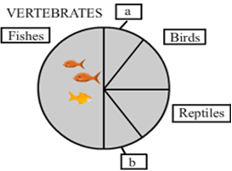
Short Answer TypeIdentify 'a' and 'b' in the figure given below representing proportionate number of major vertebrate taxa.
Explain Darwinian theory of evolution with the help of one suitable example. State the two key concept of the theory.
State a reason for the increased population of dark coloured moths coinciding with the loss of lichens (on tree barks) during industrialization period in England.
Identify the examples of convergent evolution from the following:
(i) Flippers of penguins and dolphins
(ii) Eyes of octopus and mammals
(iii) Vertebrate brainsWith the help of any two suitable examples explain the effect of anthropogenic actions on organic evolution.
Write the similarity between the wing of a butterfly and the wing of a bat. What do you infer from the above with reference to evolution?
State the theory of Biogenesis. How does Miller’s experiment support this theory?
The theory or law of biogenesis was proposed by Louis Pasteur. He proposed that all life originated from pre-existing life. These cells further originated from the organic compounds. So, ultimately life could have come from pre-existing non-living organic molecules (e.g. RNA, protein, etc.) and that formation of life was preceded by chemical evolution, i.e., formation of diverse organic molecules from inorganic constituents. In 1953, Urey and Miller conducted an experiment to prove this theory. They created the conditions of primeval earth − high temperature, volcanic storms, reducing atmosphere containing CH4, NH3, etc at laboratory scale. They then stimulated electric discharge in a closed flask containing CH4, H2, NH3 and water vapour at 8000°C. They observed formation of amino acids.
In similar experiments, others observed, formation of sugars, nitrogen bases, pigment and fats. These small organic molecules are the building blocks for proteins & other components. Hence, this experiment supported that life has come from pre-existing non-living organic molecules.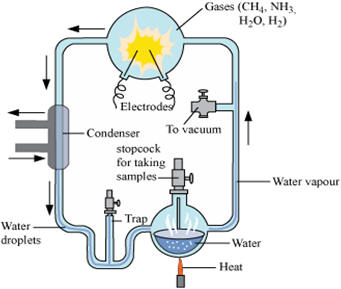
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type