 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
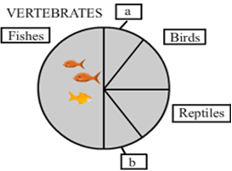
Short Answer TypeIdentify 'a' and 'b' in the figure given below representing proportionate number of major vertebrate taxa.
Explain Darwinian theory of evolution with the help of one suitable example. State the two key concept of the theory.
State a reason for the increased population of dark coloured moths coinciding with the loss of lichens (on tree barks) during industrialization period in England.
Identify the examples of convergent evolution from the following:
(i) Flippers of penguins and dolphins
(ii) Eyes of octopus and mammals
(iii) Vertebrate brainsWith the help of any two suitable examples explain the effect of anthropogenic actions on organic evolution.
Write the similarity between the wing of a butterfly and the wing of a bat. What do you infer from the above with reference to evolution?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type