 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeAction filament :
1. Each actin (thin) filament is made of two “F” (filamentous) actins helically wound to each other. Each ‘F’ actin is a polymer of monomelic ‘G’ (Globular) actins.
2. Two filaments of another protein, tropomyosin also run close to the ‘F’ actins throughout its length.
3. A complex protein troponin is distributed at regular intervals on the tropomyosin.
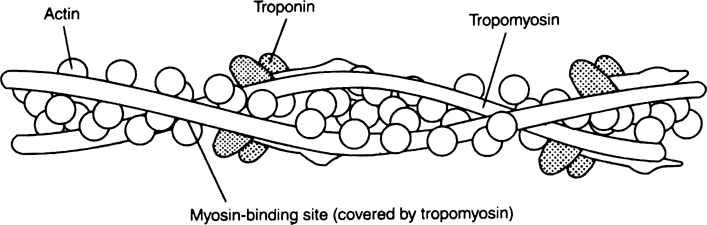
Structure of thick and thin filaments
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Match The Following
Match The FollowingMatch Column I with Column II :
| A. Smooth muscle | (i) Myoglobin |
| B. Tropomyosin | (ii) Thin filament |
| C. Red Muscles | (iii) Sutures |
| D. Red Muscles | (iv) Involuntary |
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsLack of relaxation between successive stimuli in sustained muscle contraction is known as
fatigue
tetanus
tonus
tonus
Which type of tissue correctly matches with its location?
| Tissue | Location |
| Areolar tissue | Tendons |
| Tissue | Location |
| ATransitional epithelium | Teip of nose |
| Tissue | Location |
| Cuboidal epithelium | Tlining of stomach |
| Tissue | Location |
| Cuboidal epithelium | Tlining of stomach |
The H -zone in the skeletal muscle fibre is due to
the absence of myofibrils in the central portion of A-band
the central gap between myosin filaments in the A-band
the central gap between actin filaments extending through myosin filaments in the A-band
the central gap between actin filaments extending through myosin filaments in the A-band
Select the correct statement with respect to locomotion in humans
A decreased level of progesterone cause osteoporosis in old people
Accumulation of uric acid crystals in joints causes their inflammation.
The vertebral column has 10 thoracic
The vertebral column has 10 thoracic
