 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeThe sliding filament theory explains the mechanism of muscle contraction. A proposed mechanism of muscle contraction in which the actin and myosin filaments of striated muscle slide over each other to shorten the length of the muscle fibres (see sarcomere). Myosin-binding sites on the actin filaments are exposed when calcium ions bind to troponin molecules in these filaments. This allows bridges to form between actin and myosin, which requires ATP as an energy source. Hydrolysis of ATP in the heads of the myosin molecules causes the heads to change shape and bind to the actin filaments. The release of ADP from the myosin heads causes a further change in shape and generates mechanical energy that causes the actin and myosin filaments to slide over one another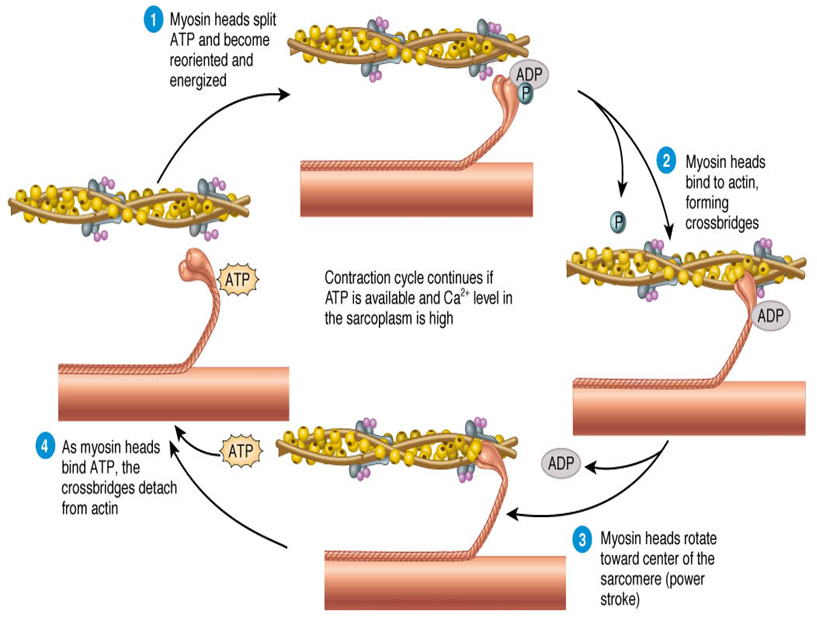
 Match The Following
Match The FollowingMatch Column I with Column II :
| A. Smooth muscle | (i) Myoglobin |
| B. Tropomyosin | (ii) Thin filament |
| C. Red Muscles | (iii) Sutures |
| D. Red Muscles | (iv) Involuntary |
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsLack of relaxation between successive stimuli in sustained muscle contraction is known as
fatigue
tetanus
tonus
tonus
Which type of tissue correctly matches with its location?
| Tissue | Location |
| Areolar tissue | Tendons |
| Tissue | Location |
| ATransitional epithelium | Teip of nose |
| Tissue | Location |
| Cuboidal epithelium | Tlining of stomach |
| Tissue | Location |
| Cuboidal epithelium | Tlining of stomach |
The H -zone in the skeletal muscle fibre is due to
the absence of myofibrils in the central portion of A-band
the central gap between myosin filaments in the A-band
the central gap between actin filaments extending through myosin filaments in the A-band
the central gap between actin filaments extending through myosin filaments in the A-band
Select the correct statement with respect to locomotion in humans
A decreased level of progesterone cause osteoporosis in old people
Accumulation of uric acid crystals in joints causes their inflammation.
The vertebral column has 10 thoracic
The vertebral column has 10 thoracic
