 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeArrange the following compounds in increasing order of their acid strength.
Propan-1-ol, 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol, 3-nitro-phenol, 3, 5-dinitrophenol, phenol, 4-methyl phenol.
When any phenol loses its acidic proton, it forms an oxygen with three lone pairs. In phenol, these lone pairs can be dislocated over the aromatic ring, providing resonance stability. This added stability allows for the easier dissociation of phenols. Thus, order of acidity is ,
Propan-1-ol < 4-methyl phenol, phenol <3-nitrophenol < 3, 5-dinitrophenol < 2, 4, 6-tri nitro-phenol.Why has tertiary alcohol higher reactivity towards hydrogen halide compared to secondary and primary alcohols?
State what happens when isopropyl chloride is boiled with alcoholic potassium hydroxide solution.
Which electrophile is the attacking reagent when phenol and chloroform undergoes Reimer Tiemann reaction?
Write the structure of the major product and also label the product as 1°, 2° or 3° alcohol.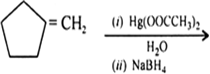
Name the enzymes which convert sucrose into glucose and fructose and finally into ethanol.
Arrange the following compounds in order of increasing boiling points:
Penta-1-ol, butan-1-ol, butan-2-ol, ethanol, propan-1-ol, methanol.
