 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeGive a brief description of the principles of the following techniques taking an example in each case.
(a) Crystallisation (b) Distillation
(c) Chromatography
Crystallisation:
This is a most common method for the purification of solid organic compounds. It is based on the fact that certain organic compounds are partly soluble in a solvent at room temperature and solubility increases with increases in temperature. Example: separation of sugar from a mixture of sugar and common salt by using ethanol.
Distillation:
This method is based on the principle that at constant pressure every pure liquid boils at a definite temperature called its boiling point. The method is used for the purification of those liquids which boil without decomposition provided the impurities are non-volatile. The method is applied for the purification when the two liquid differs in the boiling points by 30-50K.
Chromatography
The technique dependes on the distribution of the mixture between two phases, one fixed and the other mobile. The fixed phase may bean absorbent column (a solid chemical compound) or a paper strip. The moving phase may be a liquid or gas. the mixture to be separted is dissolved in the moving phase and passed over the fixed phase. There are three types of chromatography.
i) adsorption chromatography
ii) partition chromatography
iii) gas chromatography
Discuss the principle of estimation of halogens, sulphur and phosphorus present in an organic compound.
Why is nitric acid added to sodium extract before adding silver nitrate for testing halogens?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeIn the organic compound CH2 = CH – CH2 – CH2 – C ≡ CH, the pair of hybridised
orbitals involved in the formation of: C2 – C3 bond is:
(a) sp – sp2
(b) sp – sp3
(c) sp2 – sp3
(d) sp3 – sp3
 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsPresence of nitrogen in which among the following compounds can not be detected by Lassaigne method?
Hydrazine
Aniline
p-toluidine
Picric acid
The hottest region of Bunsen flame shown in the figure below is: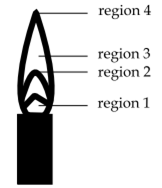
region 2
region 3
region 4
region 4
The distillation technique most suited for separating glycerol from spent-lye in the soap industry is:
fractional distillation
steam distillation
distillation under reduced pressure
distillation under reduced pressure
Which branched chain isomer of the hydrocarbon with molecular mass 72u gives only one isomer of mono substituted alkyl halide?
Tertiary butyl chloride
Neopentane
Isohexane
Isohexane
Identify the compound that exhibits tautomerism
2-Butene
Lactic acid
2-Pentanone
2-Pentanone
